Advanced Nuclear Engineering
& Technological Innovation
Sandia provides world-class scientific, engineering, and cyber solutions that foster safer, more secure management of nuclear materials and capabilities.
Nuclear Material Storage and Transportation
Sandia leverages state-of-the-art capabilities within the U.S. national lab complex, industry, academia, and with international collaborators to provide experimental, analytical, and modeling tools, data, and analyses to the U.S. government to make decisions and communicate the safety of long-term storage and subsequent transportation of spent nuclear fuel.
For more information, click here.

Nuclear Material Deep Borehole and Geologic Disposal

Sandia performs research on systems engineering processes and postclosure safety assessment methods to plan, develop, implement, and evaluate deep geologic disposal facilities for spent nuclear fuel (SNF) and high-level radioactive waste (HLW). Geologic disposal options for nuclear waste include mined repository concepts in salt, argillite, and crystalline rock and borehole disposal.
Sandia conducts experimental studies, develops process models, and performs quantitative and qualitative analyses to further the scientific basis to safely dispose of nuclear waste. Our goal is to provide world-class leadership in deep geologic disposal research and development. For more information on deep borehole and deep geologic disposal, click here.
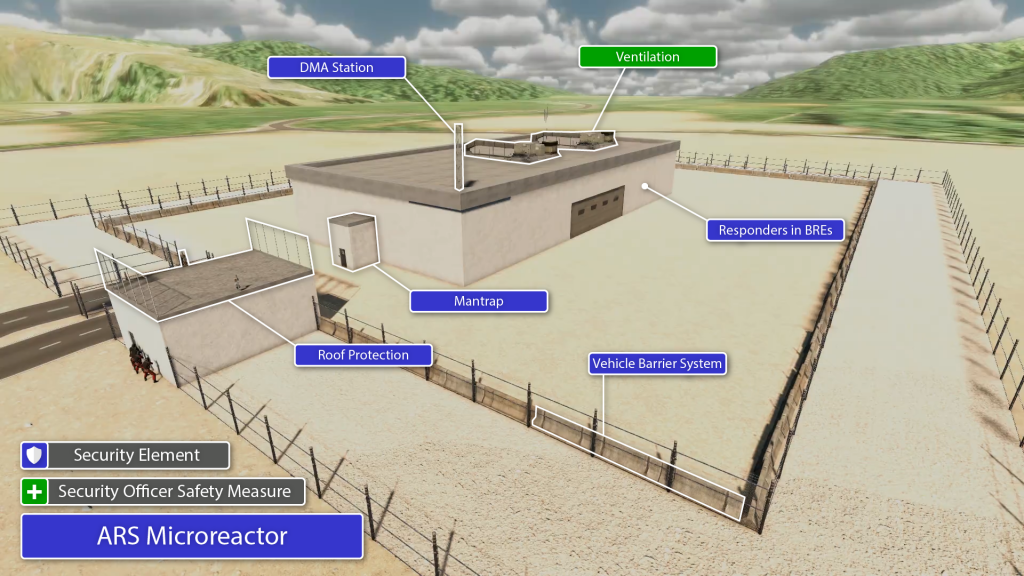
Safety, Security & Safeguards by Design Tools
Sandia leads in Safety, Security, and Safeguards by Design (3SBD), which is an innovative approach to nuclear reactor design that integrates these elements early in the process in order to optimize design and prevent costly retrofits at nuclear facilities. As part of Department of Energy and National Nuclear Security Administration programs, Sandia is partnering with reactor vendors to provide technical recommendations for design and regulatory considerations for domestic and international deployment. Sandia uses a variety of modeling and simulation tools for 3SBD including PathTrace and Scribe3D.
For information on each of these tools, click here.
Revolutionizing Safeguards Inspections
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) relies on safeguards to ensure the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons. Safeguards are measures and procedures implemented to verify that nuclear materials are used for peaceful purposes and not diverted for military or unauthorized purposes. One important aspect of safeguards is the use of tamper-indicating devices. These devices are used to indicate any tampering or unauthorized access to containers holding nuclear material.
Bleeding Materials
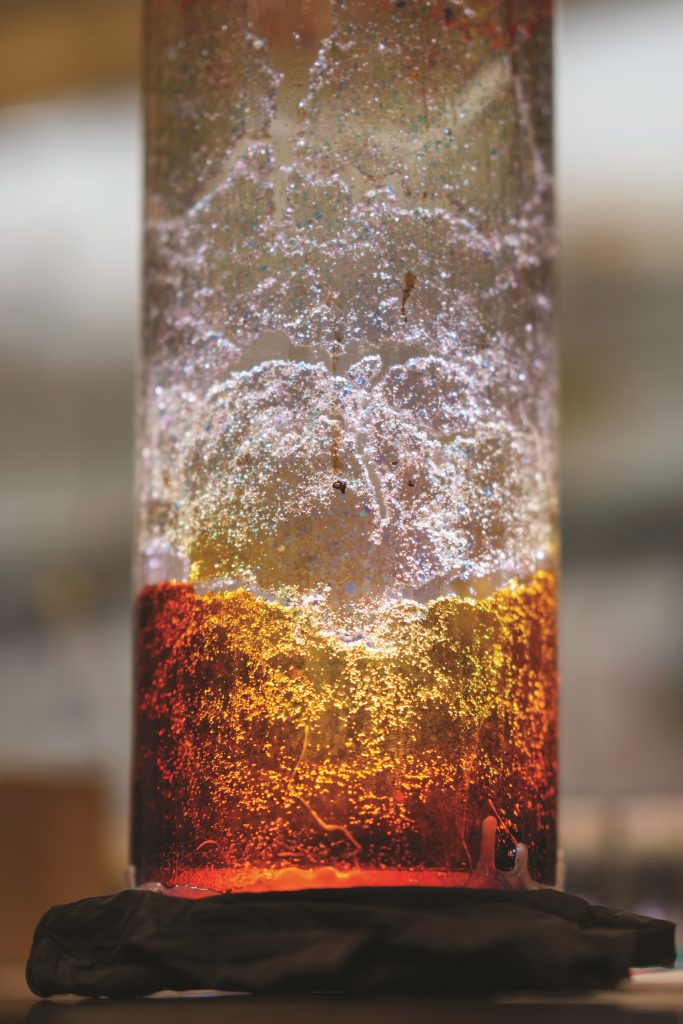

Engineers at Sandia have developed a groundbreaking prototype tamper-indicating device using “bruising” materials. This device not only detects tampering but also visibly displays the evidence. The color-changing solution used in the device contains a chemical called L-DOPA, which reacts with oxygen to produce melanin, resulting in a brown color change. If someone attempts to drill a hole in the device or pull out the wires, oxygen leaks in, causing the color-changing solution near the damage to turn brown. Over time, the “bruise” grows as more oxygen enters the device.
About the size of a stack of seven U.S. half-dollar coins, the prototype devices are being tested under various conditions to ensure their effectiveness. The goal is to reduce the time and subjectivity of inspections by IAEA inspectors. Click here to read a recent LabNews article on this technology.
Inspecta with Spot the Robot Dog

Inspecta is an AI-enabled smart digital assistant with robotic support for increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of international nuclear safeguards inspections. Safeguards inspections are challenging due to hazardous radiation environments, the need for inspectors to wear full personal protective equipment, and the variety and quantity of tasks that safeguards inspectors must perform in a limited amount of time. Inspecta and Spot the Robot Dog offer the following capabilities:
- Optical character recognition for reading and digitizing seal IDs
- Natural language processing and speech synthesis enabling Inspecta to take notes, set timers, etc.
- Information recall about previous inspections, equipment, safeguards definitions, or task steps
- Wayfinding using LiDAR to create maps of facilities and set waypoints
- Object detection using cameras and AI datasets
Click here for the factsheet.
Cooperative Scientific Engagement
in the Third Nuclear Age
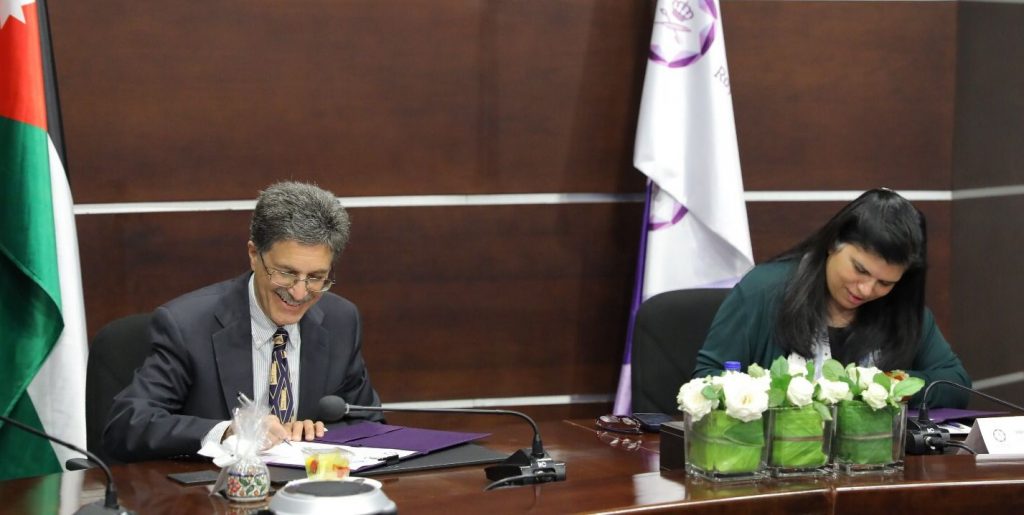

Since its founding at Sandia National Laboratories in 1994, the CMC has used cutting-edge science, engineering, and technology to build cooperative engagements around the world to strengthen international security. Recent CMC efforts include the signing of a Letter of Intent between CMC Managing Director Amir Mohagheghi and Princess Sumaya bint El Hassan, president of Jordan’s Royal Scientific Society (RSS), to enhance Sandia-RSS collaboration in areas of mutual interest. Carrying out joint research and development projects and undertaking capacity building efforts are key elements of the CMC’s relationship with the RSS. For example, the Radiation Measurements Cross Calibration (RMCC) project will support and develop cooperative efforts across the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region by establishing shared internationally recognized standards for laboratory analytical radiation measurements.
For more information on the CMC’s recent activities and speaker series, visit cmc.sandia.gov.