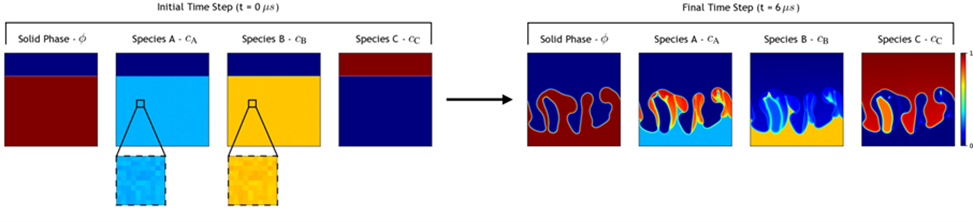
News Article, March 3, 2025 • Liquid metal dealloying. The initial species fields (cA and cB at t=0) are contaminated with low-amplitude random white noise (left fields). Given the chaotic nature of the dealloying process, the initial noise perturbation eventually leads to widely different solid phase fields at late time (e.g., right fields, at t=6μs, after 6 million time steps). When...