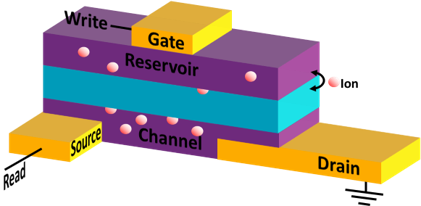
Data-heavy workflows such as AI require in to increase system efficiency. Work on this memory computing, so this LDRD team focused on creating analog resistive nonvolatile memory to increase system efficiency. Work on this project revealed fundamental principles of an electrochemical random-access memory, established a viable path toward its integration, and leveraged correlated phenomena to enable on-demand architectural reconfigurability of computing fabrics. Anticipated impacts include computing systems with orders of magnitude improved energy efficiency and radiation hardness. This project resulted in three Technical Advances and six publications, including “Nonvolatile Electrochemical Random-Access Memory under Short Circuit” published in Advanced Electronic Materials and “Filament Free Bulk Resistive Memory Enables Deterministic Analogue Switching” published in Advanced Materials. The project benefited from collaborations with faculty and students at Sandia Alliance partner UT Austin, Sandia National/Regional partner University of Michigan, and faculty at Sandia Alliance partner Texas A&M University, and Sandia National/Regional partners Stanford and Arizona State University. The Science Magazine Board of Reviewing Editors appointed PI Alec Talin to the board for his demonstrated expertise.
Sandia researchers linked to work
- A. Alec Talin
- Elliot Fuller
- Matthew Marinella
- Joshua Sugar
- Francois Leonard
Sponsored by

Associated Publications
Berggren, K., Xia, Q., Likharev, K. K., Strukov, D. B., Jiang, H., Mikolajick, T., Querlioz, D., Salinga, M., Erickson, J. R., Pi, S., Xiong, F., Lin, P., Li, C., Chen, Y., Xiong, S., Hoskins, B. D., Daniels, M. W., Madhavan, A., Liddle, J. A., … Raychowdhury, A. (2020). Roadmap on emerging hardware and technology for machine learning. Nanotechnology, 32(1), 012002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aba70f
Li, Y., Xiao, T. P., Bennett, C. H., Isele, E., Melianas, A., Tao, H., Marinella, M. J., Salleo, A., Fuller, E. J., & Talin, A. A. (2021). In situ parallel training of analog neural network using electrochemical random-access memory. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.636127
Talin, A. A. (2020). A novel metal-to-insulator transition found promising for neuromorphic computing. Matter, 2(5), 1079–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2020.04.013
Li, Y., Fuller, E. J., Sugar, J. D., Yoo, S., Ashby, D. S., Bennett, C. H., Horton, R. D., Bartsch, M. S., Marinella, M. J., Lu, W. D., & Talin, A. A. (2020). Filament‐free bulk resistive memory enables deterministic analogue switching. Advanced Materials, 32(45), 2003984. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202003984
Fuller, E. J., Ashby, D. S., Polop, C., Salagre, E., Bhargava, B., Song, Y., Vasco, E., Sugar, J. D., Albertus, P., Menteş, T. O., Locatelli, A., Segovia, P., Gonzalez-Barrio, M. Á., Mascaraque, A., Michel, E. G., & Talin, A. A. (2022). Imaging phase segregation in nanoscale lixcoo2 single particles. ACS Nano, 16(10), 16363–16371. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c05594
Kim, D. S., Watkins, V. J., Cline, L. A., Li, J., Sun, K., Sugar, J. D., Fuller, E. J., Talin, A. A., & Li, Y. (2022). Nonvolatile electrochemical random‐access memory under short circuit. Advanced Electronic Materials, 9(1), 2200958. https://doi.org/10.1002/aelm.202200958