
New system enables remote study of Arctic seafloor
Sandia scientists are using an existing fiber optic cable off Oliktok Point on the North Slope of Alaska to study the conditions of the Arctic seafloor out to 20 miles from shore. The team has developed a system to remotely collect data using a single fiber strand. The data is useful in understanding the distribution of submarine permafrost and how it changes over time. • 8000

WIPP replacement panels performance assessment
Sandia completed a performance analysis in support of the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant’s Replacement Panels Planned Change Request, which was submitted to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency for approval in March 2024. This analysis evaluated the long-term performance of the WIPP repository using a proposed configuration that incorporates additional waste disposal panels into the current repository design. EPA approval of the request will allow WIPP to continue disposal of the legacy defense-related transuranic waste from storage sites across the country. • 8000
Computing expertise informs national security policy
Through the interagency program Software Understanding for National Security, experts from Sandia’s Homeland Security Program informed federal efforts to coordinate and develop better understanding of software threats, identify needs for research and development, and form policy recommendations. Sandia supported Department of Homeland Security workshops and provided guidance to the new White House interagency office. Labs experts delivered a research and development roadmap to the department, outlining priorities and paving the way for future efforts. • 5000, 8000, 9000
Cybersecurity process for nuclear reactors
Sandia delivered draft guidance to the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission that could help bring more advanced and small modular nuclear reactors online. The guidance offers a tiered cybersecurity-by-design approach, allowing potential relaxations in physical security requirements in advanced reactors, compared to current large light-water reactors. Sandia plays a vital role for the NRC in development of the technical foundational elements for this guidance, a product of work by a multidisciplinary team from multiple centers in support of the Nuclear Energy Safety and Security Center. • 8000

Machine-learning algorithms work to minimize wildfires
Sandia developed a new way to run wildfire simulations that characterize ground vegetation. These new machine-learning algorithms, coupled with real-time weather data, will help utilities understand risks near electrical infrastructure and prioritize vegetation management to minimize wildfires ignited by the electrical grid. The work capitalizes on partnerships with the Public Service Company of New Mexico and the U.S. Forest Service to better understand the risks of grid-initiated wildfires, including wildfire identification, simulated fire response to fuel treatments and impacts to the grid and surrounding communities. • 6000, 8000
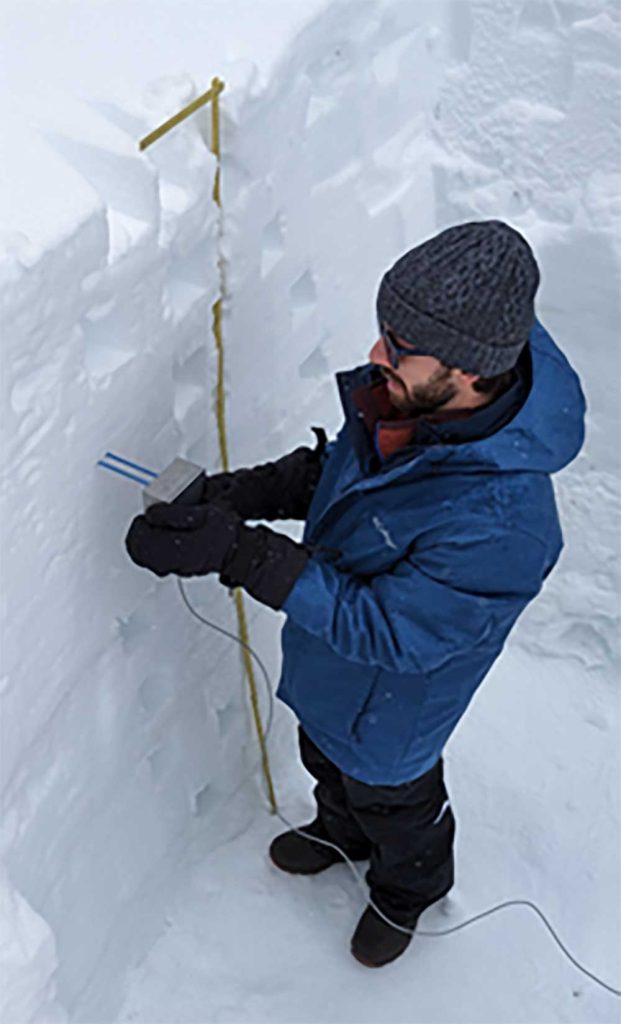

Sensor revolutionizes snowpack analysis
Sandia developed an innovative solid-state impedance spectroscopy snow density and liquid fraction sensor. Prototype testing, in collaboration with University of California, Berkeley’s Sierra Snow Lab, surpassed existing market solutions. The technology paves the way for advanced commercial products and field-deployable arrays capable of assessing snowpack conditions in detail, including liquid-water fraction and ice density, while addressing how it could affect national security and water resources. • 8000

AI enables malware threat detection
Culminating a seven-year partnership, Sandia’s Homeland Security Program provided a suite of sophisticated analytic tools to the Department of Homeland Security that improve the discovery and analysis of advanced persistent malware threats. Using advances in artificial intelligence, the team developed a novel machine-learning approach to threat discovery without known indicators of compromise, enabling earlier detection and response to cybersecurity threats. The results have been shared with industry and government partners. • 5000, 8000, 9000
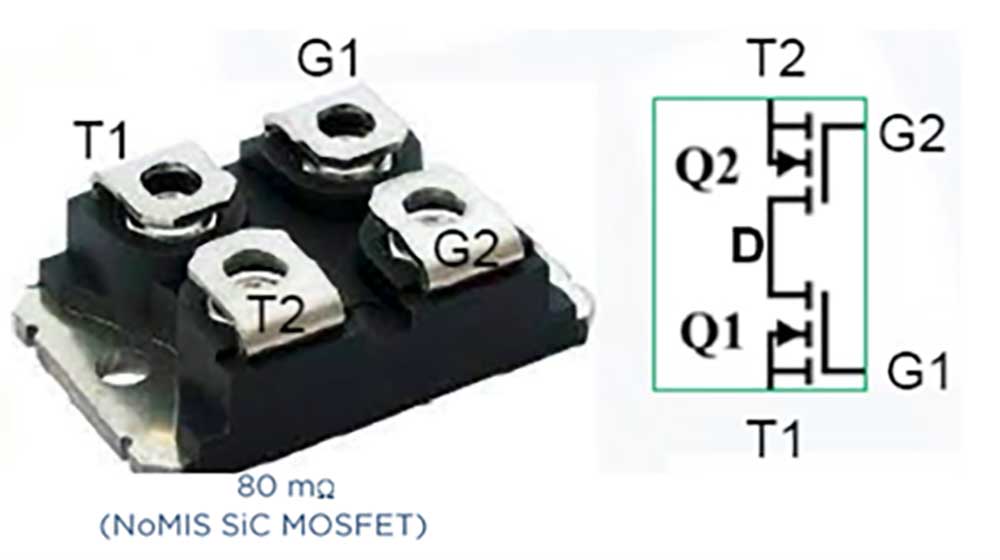
First 3.3 kV, silicon-carbide bidirectional switch
Sandia developed the world’s first single, integrated, silicon-carbide bidirectional field effect transistor with a voltage rating greater than 3 kilovolts, enabling the next generation of high-power energy conversion systems for the electric grid and many other applications. Researchers demonstrated on-resistance of 400 megaohms. This new development increased the voltage rating for bidirectional field effect transistors beyond what was previously demonstrated and set a record. • 1000, 8000

Partnership enables hydrogen-powered
rail transportation
Sandia completed a risk assessment of the design and refueling infrastructure for a hydrogen-powered locomotive and tender as part of a cooperative research and development agreement with Wabtec Industries. The work enables Wabtec’s near-term deployment of hydrogen-powered locomotives and will inform regulators about developments, needs and gaps in the hydrogen-powered rail transportation sector. • 8000

Satellite data sheds light on changing Arctic
Researchers collaborated with the U.S. Space Force to obtain access to unpublished data from GPS satellite radiometers to study the loss of sea ice due to sunlight reflectivity as part of an innovative, comprehensive examination of year-to-year effects in the Arctic region. • 6000, 8000
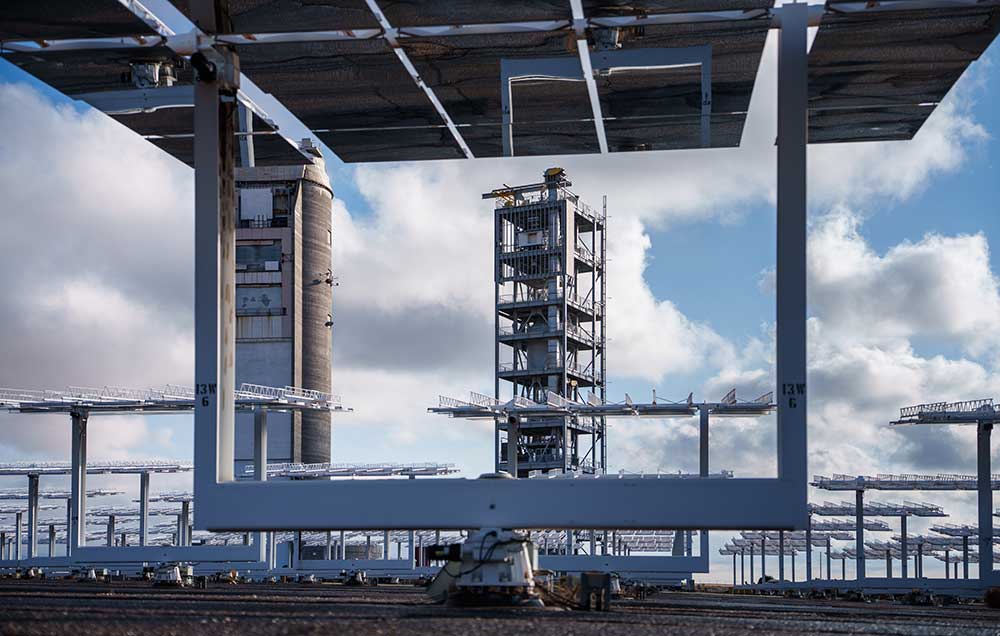

Next-generation solar power facility
Particle-based concentrating solar power can provide economical, large capacity, long duration energy storage for the electrical grid. Sandia safely completed DOE’s next-generation concentrating solar pilot plant on schedule. Testing of the fully integrated tower could begin soon and continue through summer 2025. Expanded testing at the National Solar Thermal Test Facility will help demonstrate critical technologies for a more secure U.S. energy portfolio. • 8000