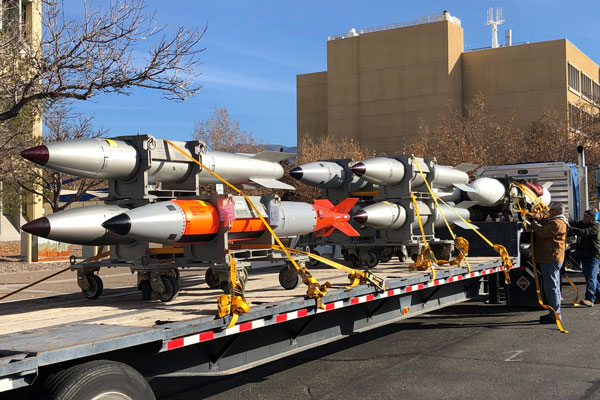

B-2 Aircraft test success
B-2 Aircraft Monitor and Control testing was completed using a full load B61-12 weapon simulator. This was the first time a full load of digital interface weapons has been demonstrated on the B-2 bomber. The test was completed in conjunction with final AMAC testing needed to certify the weapon system. (2000, 5000, 8000)
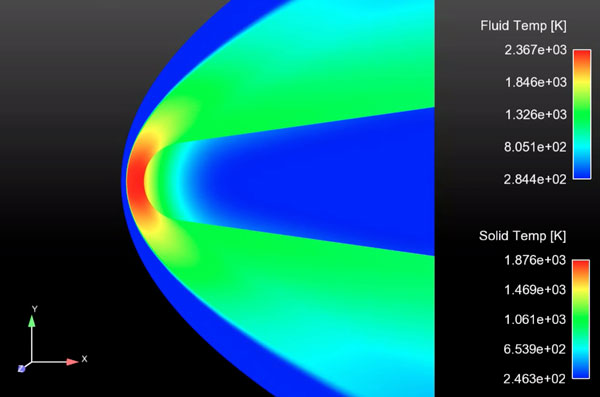
Hypersonic fluid, material response, trajectory coupling
Sandia researchers completed an effort to tightly couple the trajectory analysis code, TAOS, to their computational fluid dynamics and ablation code, SPARC. The two-way coupled capability enables the prediction of hypersonic reentry flight physics from reentry to impact and reduces the reliance on empirical models that are currently built into Sandia’s trajectory solvers. The work is part of an effort to develop a virtual flight test capability. (1000)
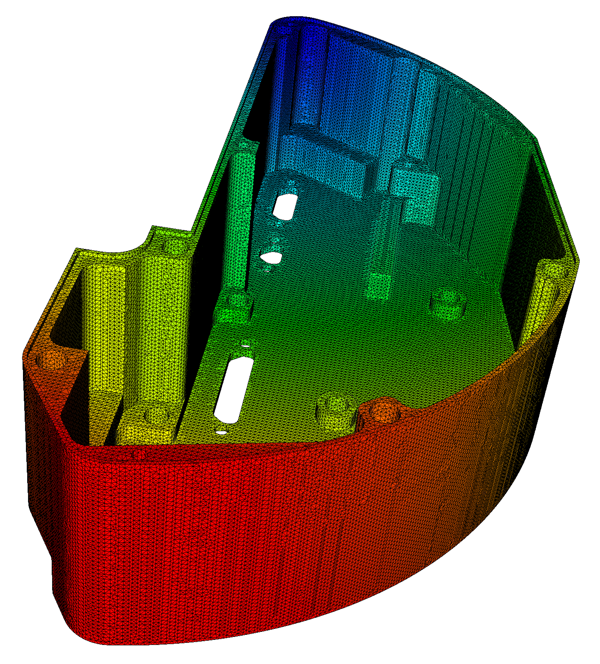
Delivering Next Generation ModSim capability
Enabling rapid computer-aided design-to-analysis workflow and generating qualification evidence via simulation are the tenets of Sandia’s Next Generation Simulation capability development project. Developed as part of NNSA’s Advanced Simulation and Computing Program, the cross-Labs team is delivering automated simulation capabilities to greatly reduce the time to produce an analysis. Two important elements are virtual design, including performance and safety assessments, and obtaining qualification evidence via simulation. Real-time user-experience testing and user-interface development are providing integrated solutions to all levels of analysts. Initial efforts have already shown months-to-minutes improvements. (1000, 2000, 6000, 8000, 10000)
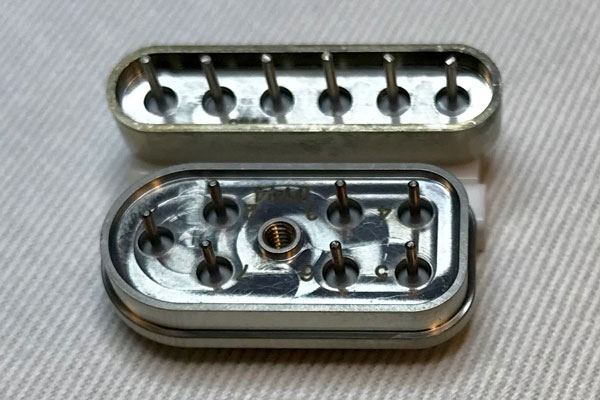

Headers produced at high yield
Sandia’s advanced science and technology and nuclear deterrence divisions collaborated to produce a critical build run of electrical headers with an incredibly high yield of 98%. Sandia was the only institution in the initial run that produced these parts to specification in a short time frame. This high yield was achieved by maintaining precise process and environmental controls established through applied materials science research and multi-disciplinary collaboration. These headers provide electrical isolation and hermiticity to internal components, ensuring that assemblies meet performance and lifetime expectations. (1000, 2000)

P19 project execution
The P19 project represents Sandia’s commitment to respond to critical national security challenges. A diverse team from across almost every division responded rapidly, contributing expertise in design, qualification, production, acceptance and fielding to meet a tight deadline. Executing the project capitalized on Sandia’s advanced capabilities and commitment to quality to deliver a solution to our DoD and NNSA stakeholders within a highly compressed schedule. The success of the P19 project clearly demonstrates Sandia’s “exceptional service in the national interest.” (2000, 6000, 5000, 8000, 9000, 10000)

Strategic Intent of Collaboration signed
The U.S. and U.K. have a rich history of cooperation dating back to the Manhattan Project. Since 1958, the countries have shared ideas, information, materials and equipment within the provisions of the Mutual Defense Agreement. In a June visit to the U.K.’s Atomic Weapons Establishment, Steve Girrens, Sandia’s associate Labs director for nuclear deterrence, and Dave Chambers, AWE’s director for science engineering and technology, on behalf of Graeme Nicholson, AWE’s head of programme, signed a Strategic Intent of Collaboration, describing and endorsing mutually beneficial opportunities for strategically aligned collaborations between Sandia and AWE. While each nation prepares for its respective future deterrence needs and maintains focus on its existing stockpiles, both Sandia and AWE recognize that through collaboration, the risk carried by each organization in delivering its mission will be reduced. (2000)
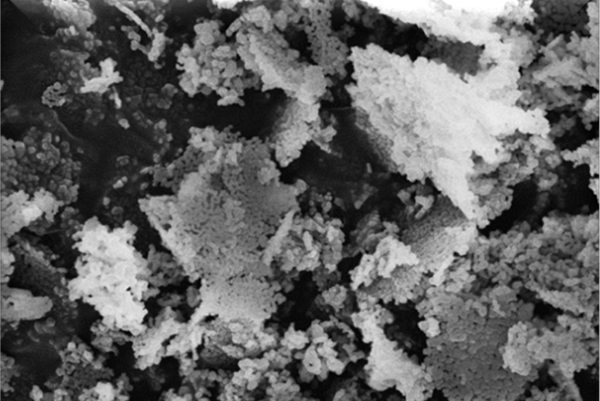
Magnesium oxide development
Sustained research and development efforts at Sandia have led to a mechanistic understanding of legacy MgO, a critical material for thermal batteries. Legacy MgO has a highly specialized nanoscale structure, critical to its function, and the supply is very limited. Failure to develop a new source of this material would adversely impact the ability to deliver thermal batteries to support current modernization or future nuclear deterrence systems. In FY19, the team demonstrated the ability to design and synthesize candidate MgOs and, for the first time, demonstrated function in prototype batteries. (2000, 1000, 6000, 9000, 10000)
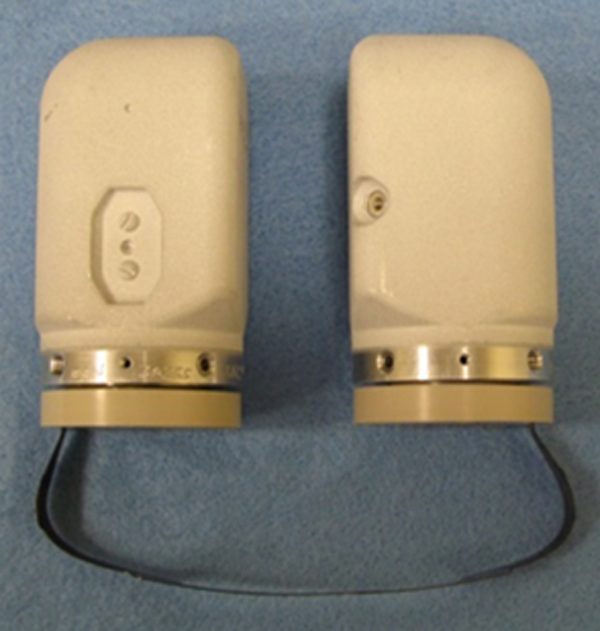

Components in full-scale development
Multiple weapons design and assurance organizations, spanning several teams and disciplines, provide critical engineering, science and business operations support for Sandia’s W80-4 program. The following components have all passed conceptual design reviews and are in full scale development: Firing Set Assembly, Firing Set Stronglink, Detonator Stronglink, magnetics, cables, connectors and commercial-off-the-shelf. (2000, 8000, 10000, 1000, 9000)
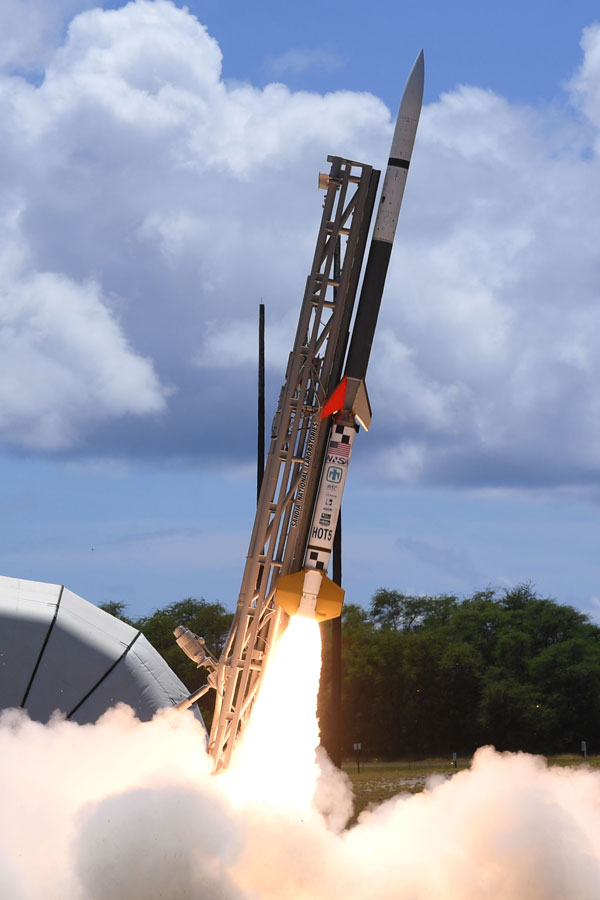

HOT SHOT program
The HOT SHOT team designed, integrated and successfully launched four payloads on Terrier-Malamute rockets in FY19. HOT SHOT flights launched out of Kauai Test Facility and carried more than 35 experiments from organizations across the Nuclear Weapons Complex, impacting the current and future U.S. stockpile. The HOT SHOT program marks NNSA’s return to rockets, providing a flexible flight-test platform to accelerate technology maturation and reduce development-cycle time, increasing the responsiveness of future modernization programs and the agility of nuclear deterrence efforts to address emerging threats. (2000, 5000)
Firing systems and controllers
Sandia’s weapons design and assurance organizations are responsible for the design, development, qualification and First Production Unit for firing systems and controllers. In FY19, the teams completed FPUs successfully and on time across the W88 ALT 370 Impact Fuze, Terminal Protection Device and Firing SubSystem, and the B61-12 Impact Sensor and PreFlight Controller. (2000)

Tonopah Test Range flight test cycle
The Sandia team at TTR compressed three normal years’ worth of technical weapons testing into 12 weeks, June to September 2019. The test team completed 17 B61-12 and stockpile surveillance flight tests, including six events in only two days, and incorporated two partner nation tests. The TTR team adjusted technical upgrades, shifted schedules, mitigated impacts and ensured 100% data capture without a single safety or security incident. During FY19, the team successfully recovered multiple test units and completed several enhancement projects. (2000)
Sandia Production milestones
Sandia Production delivered 100% of FY19 First Production Unit hardware requirements for the B61-12 LEP and W88 ALT 370 programs, including microelectronic, neutron generator, power source and explosive components. Power sources reached FPU for seven components, and explosives reached FPU for three components. These accomplishments were achieved through a combination of Sandia in-house production capabilities and outside suppliers. In addition to achieving FPU for two components, the neutron generator enterprise exceeded planned builds and met all customer shipments while staying on budget. (2000, 1000, 5000, 9000, 10000)
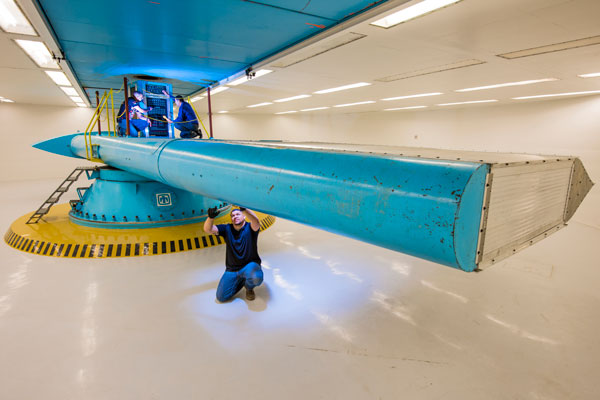

Mk21 Superfuge tests
In August 2019, the Mk21/W87 Arming and Fuzing Assembly qualification team successfully completed the first centrifuge test for record on a powered D30-pedigree AFA at Sandia’s superfuge facility. As part of the comprehensive Accumulated Damage Test, the ADT-2B test unit was mounted to the facility’s 29-foot-radius indoor centrifuge, and a combined reentry acceleration, reentry vibration and axial spin test was run on the powered and operational AFA during a simulated atmospheric reentry mission. (2000)
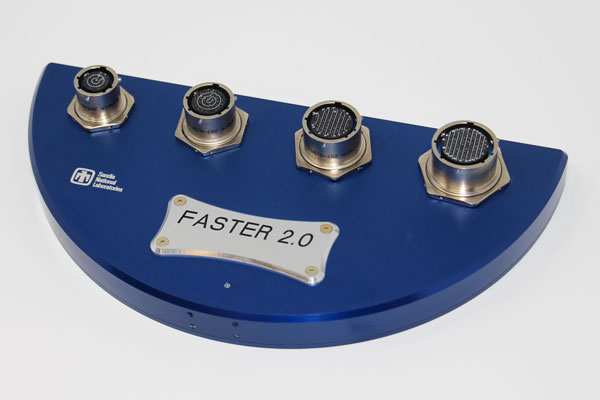

Functional AMAC System Tester 2
The Functional AMAC System Tester 2, or FASTER2, is a custom data recorder designed and built by Sandia’s handling gear and telemetry engineering team. FASTER2 is the electrical centerpiece of the B61-12 Compatibility Test Units and enables Sandia’s aircraft compatibility group to validate and certify compatibility of the interfaces between the B61-12, the Boeing Tail Kit Assembly and the delivery platforms. The FASTER2 team completed its design qualification and delivered 46 units with exceptional quality to fully support future B61-12 CTUs and ACC flight tests. (8000, 9000, 2000, 5000)

B61-12 handling gear designed, developed
Sandia’s handling gear and telemetry engineering team designed and developed 17 pieces of equipment (16 handling gear and 1 test gear), enabling the DoD customers to complete limited-life component exchanges, general maintenance and special repair operations for the B61-12. In FY19, all 17 tools achieved Qualification Engineering Release status, and the First Production Units were successfully manufactured. (8000)
Nuclear deterrence program equipment needs
In response to multiple data calls from the NNSA Programmatic Recapitalization Working Group, Sandia’s nuclear deterrence program management office led a multi-division effort creating an integrated list of programmatic capital equipment inventory and investment needs. To maintain and sustain weapon activity capabilities, the list spans the fiscal year nuclear security program period. The integrated information will provide NNSA greater transparency on actual costs, improve Sandia’s ability to prioritize investments and enable better annual budget planning, allowing superior capability maintenance. (2000, 1000, 5000, 6000, 8000, 9000)
W88 ALT 370 hostile-shock testing
HS-2, the final hostile-shock test for qualification of the W88-0/Mk5 ALT 370 Arming, Fuzing and Firing Assembly, was completed Feb. 7, 2019. HS-2 successfully exposed an AF&F assembly to a triaxial-shock loading representative of several hostile environments. The assembly was electrically functional during the hostile encounter, which verified its capability to properly fuze after exposure. Data from HS-2 will serve as the primary AF&F assembly level qualification evidence for hostile-shock environments. (2000)

Augmented Reality nuclear deterrence training
Augmented Reality is an emerging technology that offers an opportunity to blend the physical and digital worlds, allowing participants to rapidly and accurately absorb information, make decisions and execute required tasks quickly and efficiently. Sandia’s advanced science and technology organizations are exploring how AR technology can benefit U.S. nuclear deterrent activities ranging from design collaboration to nuclear weapons training. With use of a Microsoft HoloLens, Sandia created an AR training scenario to augment current hands-on B61-12 bomb disassembly training. (2000)
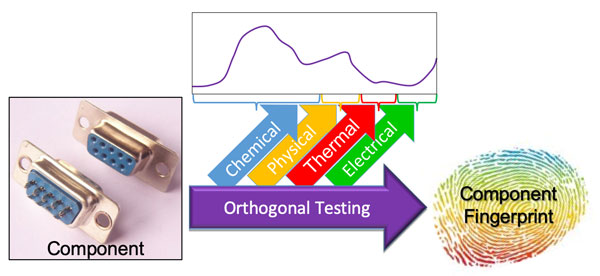
Orthogonal component testing for counterfeit detection
A cross-division team demonstrated unique component data signatures generated via fast, nondestructive and simple tests, providing a reliable method to qualify material feedstocks, identify deviations in materials manufacturing, and potentially detect changes in assembled components. Termed orthogonal testing, the method generates a robust component signature by integrating independent material properties from methodologies that operate on fundamentally different principles. While materials changes might fool a single test method, integrating independent testing nodes ensures a high-reliability signature and can instill trust in U.S. national security systems. (1000)

B61-12 Type 3C Trainer
The U.S. Air Force uses the Type 3C Trainer is a military training unit for B61-12 field maintenance, as well as limited life component exchanges. A Qualified Engineering Release for the Type 3C was released on Jan. 31, 2019, enabling Kansas City National Security Campus to complete the First Production Unit build. (2000)

New Product Introduction initiative
Sandia co-led the New Product Introduction initiative with Kansas City National Security Campus to increase design and production integration, apply lessons learned from past nuclear deterrence programs and augment nuclear deterrence development with industry best practices. This effort is accelerating progress and reducing risks in modernization programs, including the W80-4. Examples of accomplishments include creating a list of pre-approved commercial off-the-shelf electrical component parts, piloting an enhanced process for conducting technical and programmatic reviews, introducing new product development methods used in industry and facilitating design failure mode effects analysis for weapon components. (8000, 0002, 2000, 5000, 6000, 9000, 10000)

W76-2 Product Realization Team milestones
The W76-2/Mk4A Reentry Body System PRT delivered on their commitments to the U.S. Navy and NNSA, on budget and ahead of schedule. The team is on track to complete a closeout review, which will mark the end of the development and production period and will support the upcoming W76-1 closeout process. The team has successfully collaborated internally and externally to deliver with excellence and bring an orderly conclusion to the project. (2000, 9000)

B61-12 HERO testing
The B61-12 systems team successfully completed Hazards of Electromagnetic Radiation to Ordnance, or HERO, testing in FY19. The test ran from June 21-Aug. 8, 2019, completing about two weeks ahead of schedule. The two test objectives were: 1) quantifying the transfer function of Electrically Initiated Device current as a function of electric field, and 2) extrapolating the achieved margin with respect to EID minimum no-fire stimulus. (2000)
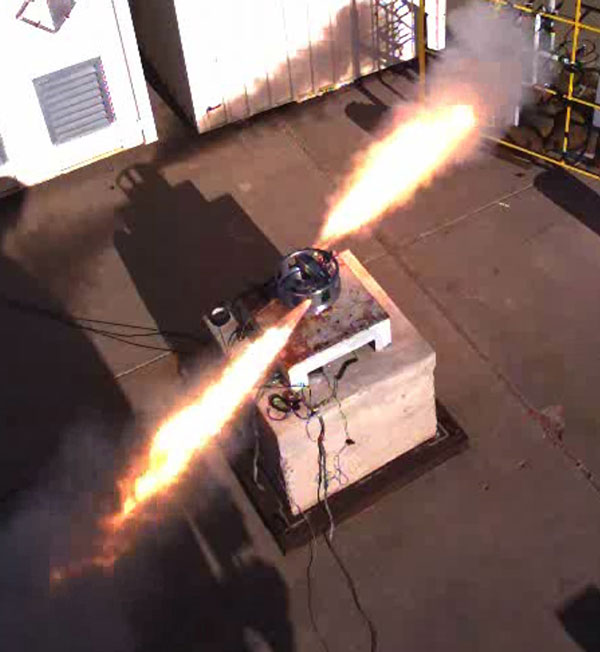
Component science, engineering and production successes
Eight neutron generator, explosive and power source components completed Qualification Evaluation Release for modernization programs in FY19. The B61-12 Spin Rocket Motor, a propellant-based energetic component, and the SRM ignitor were successfully qualified to new requirements and completed QER. The W88 ALT 370 Neutron Generator Assembly QER was released five weeks early and under budget. Three power source components were successfully qualified at an entirely new supplier in less than 18 months, and 86% of needed components have been qualified for the Mk21 program. (2000, 1000, 9000, 10000)
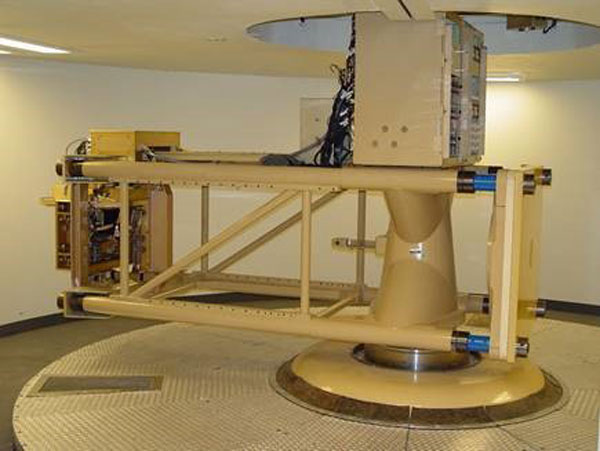

W88 ALT 370 PPI testing
In May and June 2019, testing of three W88-0/Mk5 ALT 370 Product Prove-in units was completed successfully at the Weapons Evaluation Test Laboratory. The testing simulated launch and reentry acceleration profiles while gathering key system performance data, which included 650 waveforms and 330 single-value outputs for each test. The testing provided critical evidence for the W88 ALT 370 Systems qualification program and directly supported laboratory test program qualification activities. (2000, 9000)

B61-3/4 ALT 372 delivery
Sandia successfully delivered the first seven lots of B61-3/4 ALT 372 kits to the U.S. Air Force, including achieving First Production Unit one day ahead of schedule. This was an unprecedented response to a DoD request, which required a high level of quality (Mark Quality rigor) and no impact to safety or reliability for the B61. (2000)
W88 ALT 370 Abnormal Thermal Test
The W88-0/Mk5 ALT 370 Abnormal Thermal Test, AET-3C, was successfully completed between Nov. 8-Dec. 13, 2018, at Sandia. Two Arming, Fuzing and Firing Assemblies were subjected to high-heat input comparable to an engulfing propellant fire. The primary objective was to record thermal responses internal and external to the AF&F assemblies during the test. In addition, electrical response was monitored. Both units performed as expected to ensure reliability of nuclear safety components. (2000)
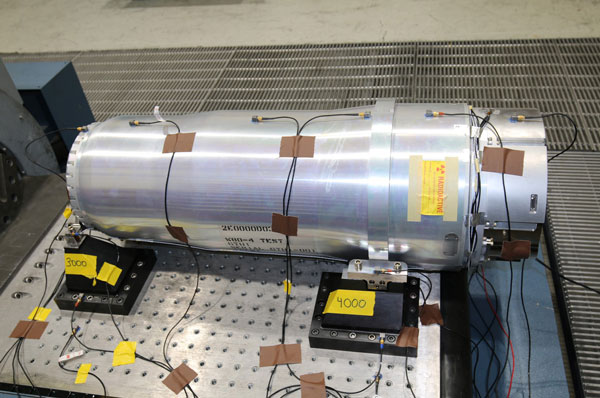
W80-4 Weapon Design and Cost Report
Sandia’s W80-4 team used programmatic processes and tools more advanced than any prior Life Extension Program to complete the WDCR. The WDCR package is a major deliverable for the Phase 6.2/6.2A period of the LEP lifecycle. Throughout this period, Sandia’s WDCR team pursued rigorous schedule and cost analysis activities using defendable, resource-loaded schedules and conducting formal Schedule and Cost, Risk and Uncertainty Analysis to estimate program cost. Their pioneering efforts resulted in an on-time delivery to NNSA of a comprehensive WDCR package, a critical step in the W80-4 LEP’s progression to the next phase of development. (8000)
W87 ALT 360 First Production Unit
The W87 ALT 360 Product Realization Team completed the Gas Transfer System FPU in January 2019, completing a six-year effort. A broad group of engineers, scientists and business professionals worked in partnership with counterparts at the production agencies (Kansas City National Security Campus and Savannah River Tritium Enterprise) to realize the design, deliver and test hardware and complete qualification activities on schedule and under budget. The new GTS meets DoD requirements while improving performance margins and extending the GTS lifetime. (8000)
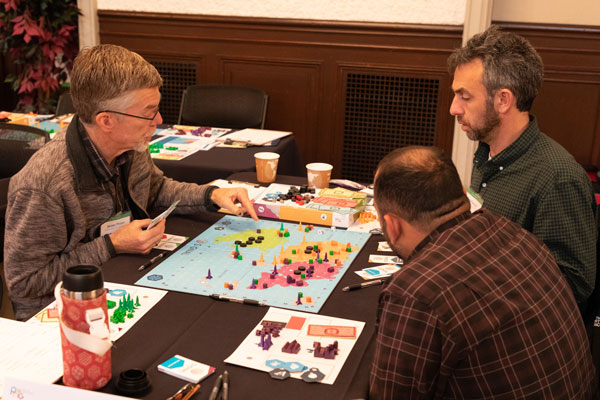

Project on Nuclear Gaming
The Project on Nuclear Gaming, or PoNG, held a workshop at the University of California, Berkeley, on Dec. 3, 2018. PoNG is a U.C. Berkeley-led project, funded by the Carnegie Corporation of New York and executed in partnership with Sandia and Lawrence Livermore national laboratories to study nuclear deterrence through analytic games. PoNG explores the use of experimental games to better understand problems of strategy, conflict and escalation. Its current focus is examining implications for strategic stability in different nuclear weapon capabilities through game environments in which players use escalation dilemmas. The 57 PoNG workshop attendees included representatives from universities, national labs, think tanks and DoD agencies. (8000)
B61-12 Radar Antenna First Production Unit
In support of the B61-12 Life Extension Program, the development and qualification cycle for bringing the B61-12 Radar Antenna through the FPU process is complete. The collaborative effort resulted in the achievement of significant milestones for this component. The Product Realization Team successfully achieved FPU status for the B61-12 Radar Antenna on April 2, 2019. The FPU milestone indicates receipt of certification from NNSA of successful completion by the production agency and subsequent yielding of the first unit to the stockpile. (5000, 2000, 6000)
W80-4 program conceptual design
The W80-4 Life Extension Program accomplished a major milestone during FY19, completing the system conceptual design review and several component conceptual design reviews. Following system conceptual design, the W80-4 undertook an effort to simplify the system design to meet schedule constraints, resulting in a revised design that balances programmatic and performance risk. The program now proceeds into the baseline design phase with a design that meets the established military performance requirements while eliminating significant schedule risk for the system and components. (8000, 2000)
Code Management System upgrade
Sandia’s CMS supports the Labs’ nuclear weapons program to keep the nation’s stockpile secure. The CMS manages Permissive Action Link codes stored in each weapon for the life of the weapon, and it must be reviewed and analyzed for correct operations by several organizations. The software also is required to obtain certification as a National Security Agency Type 1 cryptographic system. In FY19, the CMS successfully completed all required reviews and analyses to obtain NSA Type 1 certification and the Quality Assurance Inspection Procedure. Successful completion of the QAIP resulted in the DOE Diamond Stamp, required by the DoD customer prior to delivery of the software to DoD and DOE customers. Diamond Stamp was the culmination of the team’s efforts over six years and fully supports the PAL equipped weapons in the current stockpile, as well as the B61-12. (2000)
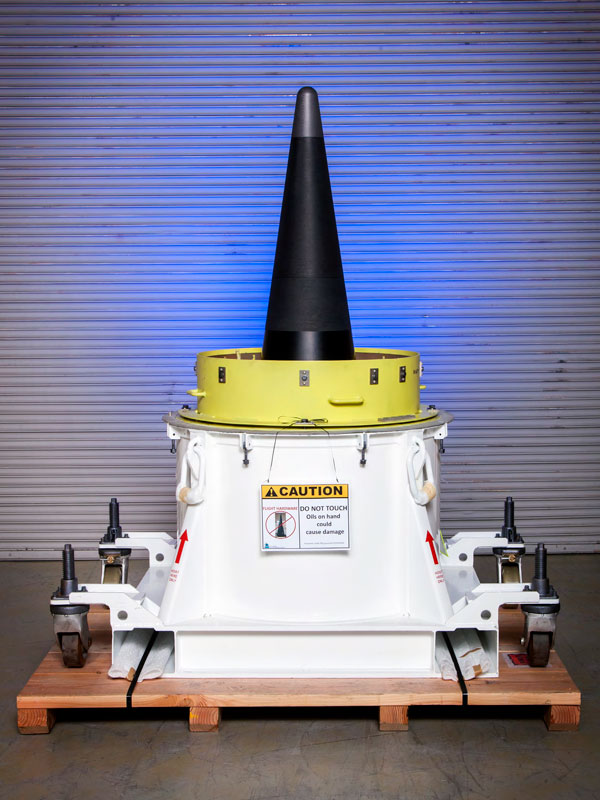

Mk21 Fuze flight test success
The Mk21 Fuze program’s first flight test vehicle, Flight Test Unit 1, was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base on a Minuteman III missile on Feb. 5, 2019. Telemetry data confirmed successful performance of the fuze and telemetry system. Completion of FTU1 was a coordinated effort across Sandia. The Mk21 Fuze program, a Strategic Partnership Program funded by the U.S. Air Force, entered phase 6.4 production engineering in January 2019. (8000, 2000, 5000)
W87-1 relaunches program, partners early
The W87-1 modernization program, paused in 2014, was back on track in FY19 with systems engineering and project management structures in place and 12 component teams and 16 mission realization partners on board. The technical team engaged in rigorous assessment of multiple design architecture options. Establishing strong partnerships early in the program is a priority for the W87-1. Sandia and Lawrence Livermore national laboratories began collaboration in January 2019. Sandia and Kansas City National Security Campus held a joint kick-off in March 2019. (8000, 2000, 1000)
Sensors detect nuclear proliferation
A Sandia team led the seismic and infrasound sensor networks that collected the primary scientific diagnostic data for the source physics experiment dry alluvium geology test series, which consisted of three underground chemical explosions conducted in FY19. (8000)