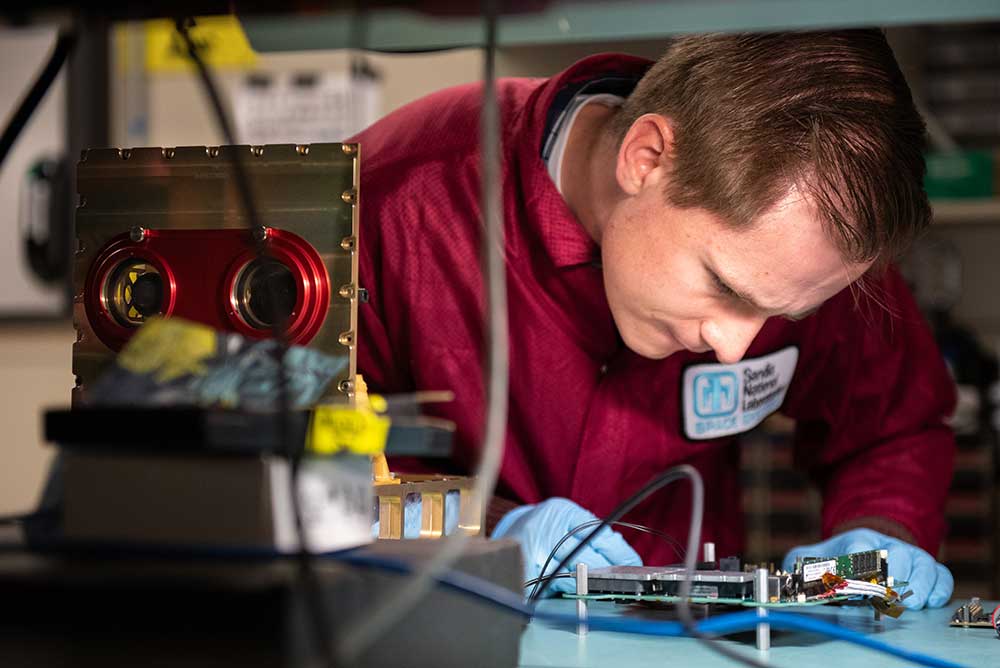
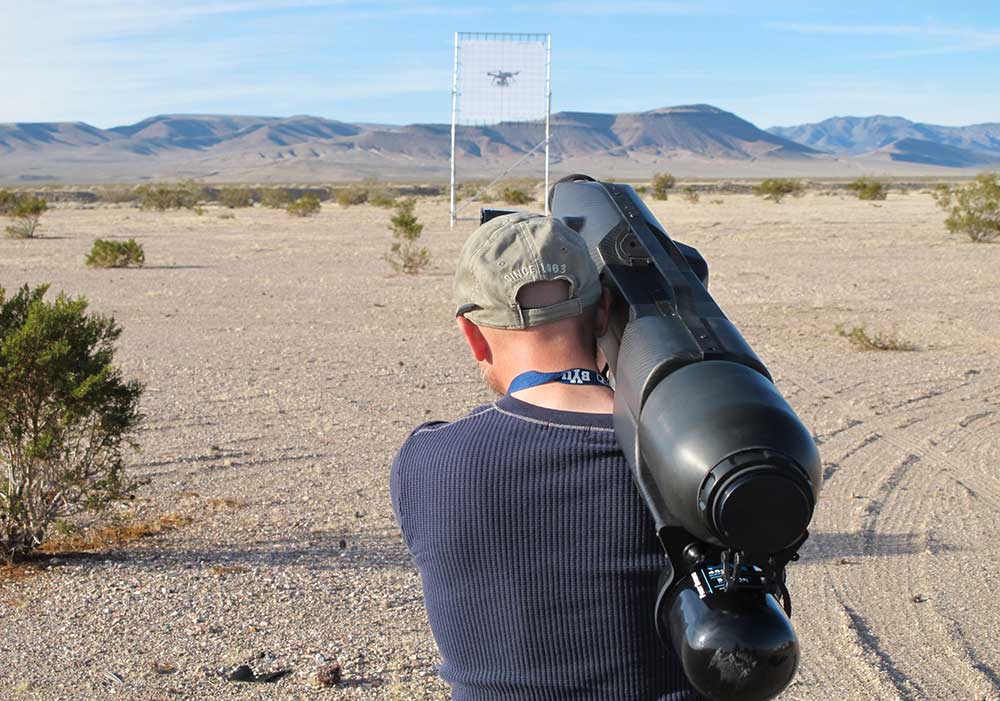
Technology tested in orbit
Sandia used the International Space Station as a proving ground to develop a process to rapidly test and mature technology in space. Astronauts installed a payload containing a computer chip with advanced processing capabilities aboard the space station to test high-performance computing technology. Testing in orbit reduces time needed to deploy national security systems and helps mature research for space readiness. Data generated from each payload hosted on the space station will ultimately enable the Sandia team to be more responsive to national security threats and opportunities. • 6000
Next-generation counter-uncrewed aircraft systems
Sandia’s Autonomy and Unmanned Systems Team developed requirements for the next generation of counter-uncrewed aircraft systems. The document will be the basis for NNSA’s acquisition and deployment strategy in fiscal years 2024-2030. The requirements included an open-architecture approach, which will allow the NNSA and its interagency partners to rapidly adapt to new technologies and address evolving threats. • 6000
The Safeguards Transporter Compatibility Retrofit achieved first production unit, with two Safeguards Transporter trailers completing installation of Integrated Surety Architecture hardware at the Kansas City NNational Security Complex-New Mexico Operations site. Integrated surety architecture provides an additional level of security for over-the-road transportation of NNSA assets. The Sandia and KCNSC-New Mexico Operations partnership will continue beyond initial qualification to complete conversion of the entire Safeguards Transporter fleet and maintain transporters through the end of fleet life. • 6000
Ground-based seismoacoustic sensors detect explosions
On behalf of NNSA and the DOD, Sandia rapidly deployed Minikin Echo, a suite of seismoacoustic sensor arrays, in Eastern Europe to detect explosives in the Russia-Ukraine war. Since the deployment, Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratory Minikin Echo teams have delivered 24/7 hardware and on-call operational support to federal leadership. The teams were recognized by the NNSA Office of Counterterrorism and Counterproliferation for their outstanding support of the nuclear forensics mission. • 6000
Ground system supports new satellite sensors
The Consolidated Overhead Ground System project delivered and tested initial operational software and hardware for commanding and processing satellite data for current and new sensors. The 100-plus person team delivered a complete hardware and software system on a high-risk schedule after a late change in acquisition approach. Despite changes to the launch schedule and scope, Sandia delivered the ground system, including 3 million lines of code, on time for successful integrated testing and new sensor checkout. • 6000

Improved accuracy for sensors over Europe
In support of U.S. European Command work in Eastern Europe, Sandia developed and deployed a hardware and software system that provides improved calibration of operational intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance sensors. This effort used years of U.S. Air Force research and development to build and integrate necessary hardware and develop real-time data processing algorithms for new calibration sources. The operational sensors can detect calibration signals in real time and increase sensor accuracy, providing critical data to decision-makers. • 6000
Secretary of Energy Achievement Award
The Afghan Rescue Team received a Secretary of Energy Achievement Award for their collaboration with the DOE and the Department of State to evacuate and relocate Afghan partners who supported chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear security nonproliferation and counterproliferation programs. This program has evacuated more than 450 partners and their families. • 6000
New application tracks waste shipments
Sandia developed the Transportation Remotely Monitored Sealing Array application to track waste shipments from the Savannah River Site to the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant. The application monitors location and assures nuclear safeguards. The director of the Office of Material Disposition designated the system as ready for use, culminating years of collaboration among Sandia, Savannah River Nuclear Solutions, the NNSA Office of Material Disposition, Kansas City National Security Campus, WIPP, Sandia Field Office and the Carlsbad Field Office. The application tracked a total of 13 WIPP shipments in fiscal year 2023. • 6000
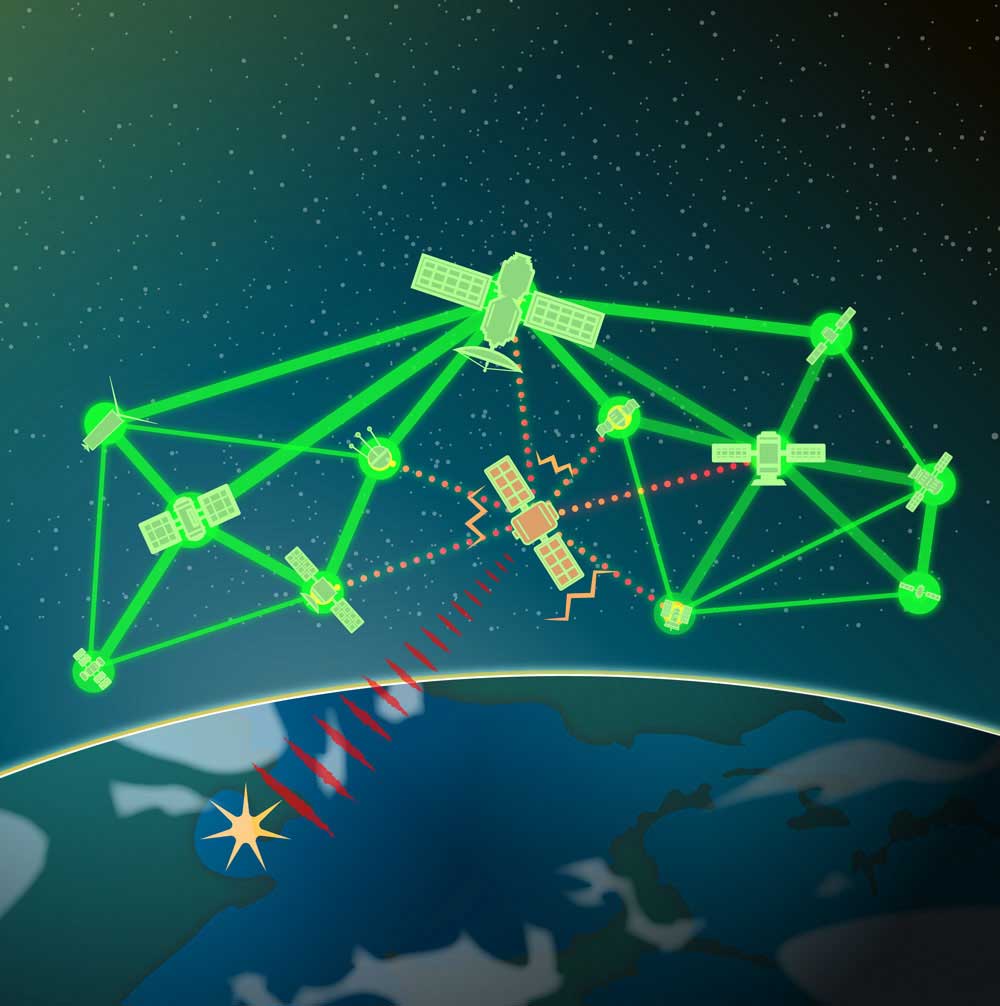
Autonomous satellites team together
A multilaboratory team demonstrated a new autonomous remote sensing solution that enables a cluster of relatively small and inexpensive satellites to work together as a single, autonomous unit. The payload prototype demonstrated command, control and data fusion architectures for space-based collection systems that are capable of processing and autonomous decision-making. Sandia’s role included developing machine learning and autonomy algorithms, radar sensors, computer models, communications protocols and flight software. • 6000
PIDS Team wins NNSA security award
Sandia and Consolidated Nuclear Security LLC received NNSA’s award for Outstanding Security Team of the Year for the successful implementation of the Portable Intrusion Detection System at the Y-12 National Security Complex. The system supports the Security Infrastructure Revitalization Program, which is refreshing the security perimeter at Y-12. The deployment allows the site to meet security requirements during the security system refresh. • 6000, Y-12
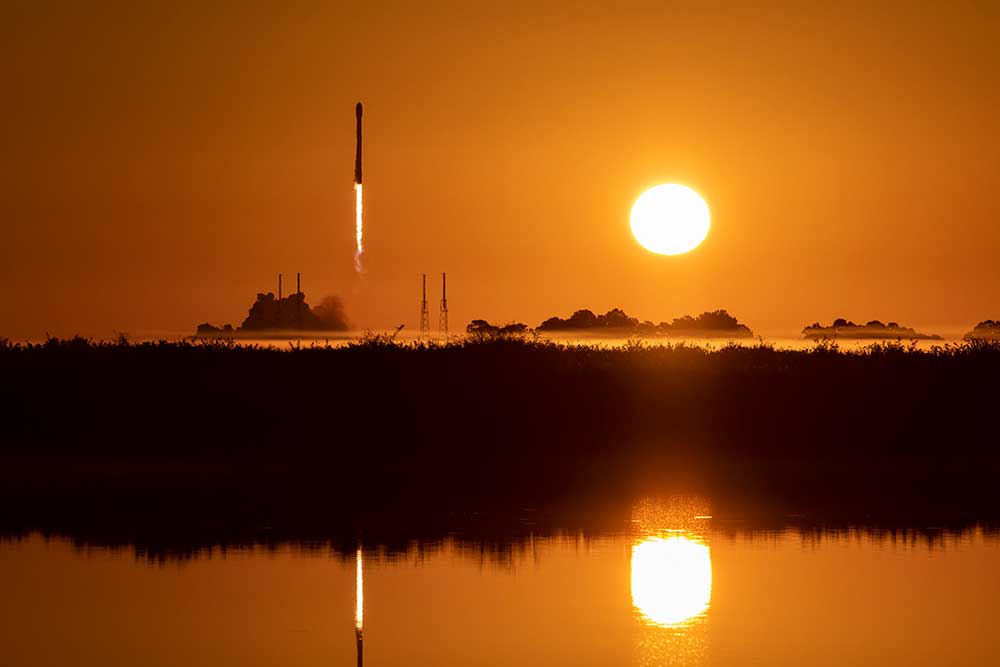

Global Burst Detector satellite operating
A Falcon-9 rocket successfully launched, delivering the satellite containing the sixth Global Burst Detector payload to its target orbit. Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratory designed and produced the payload subsystems, with Sandia as the system integrator. Sandia met major milestones to test and characterize the payload pre- and post-launch, which resulted in successful transition of the system to operations. Global Burst Detector payloads provide space remote sensing capability for the U.S. Nuclear Detonation Detection System. • 6000
New neutron detector addresses emergency response needs
A neutron detector that addresses nuclear nonproliferation and emergency response needs was developed by configuring Sandia’s organic glass scintillator into a pixelated format and integrating it with solid-state photodetectors. A detector array of more than 1,000 channels was read out using a system developed for medical imaging to achieve neutron radiographs. The new detector is more compact and rugged than current detectors and showed a twofold improvement in intrinsic neutron detection efficiency. • 8000
Detecting radiation from a remote location
Sandia demonstrated remote long-range detection and imaging of ionizing radiation at longer distances in less than a minute outdoors at night using passive nitrogen fluorescence signatures, vastly surpassing previous measurements. This meets a long-term goal of detecting radiation from a location well beyond the distance primary gamma radiation propagates and represents the farthest known demonstration of remote imaging of radioactive sources. • 6000
Mobile Guardian Transporter preproduction unit delivered to KCNSC
Sandia successfully completed initial modifications to the Mobile Guardian Transporter preproduction unit rolling chassis and delivered it on time to Kansas City National Security Campus-New Mexico Operations site. The effort included small and large modifications to internal and external mechanical interfaces to support future subsystem integration by KCNSC-New Mexico Operations. After the preproduction unit assembly is complete, it will return to Sandia to serve as the Mobile Guardian Transporter program’s primary system qualification platform and continue as the permanent test and evaluation platform for the transporter fleet. • 6000
Uranium isotope neutron signatures demonstrated
Novel neutron signatures of uranium-233 were demonstrated at the National Criticality Experiments Research Center in Nevada as a proof of concept for future nuclear safeguards techniques. The passive fast-neutron spectrum of kilogram-scale uranium-233 oxide was measured, in addition to two active interrogation signatures: differential die-away and delayed neutron time profile. The demonstrations address a high-priority area for the nuclear safeguards community. • 8000
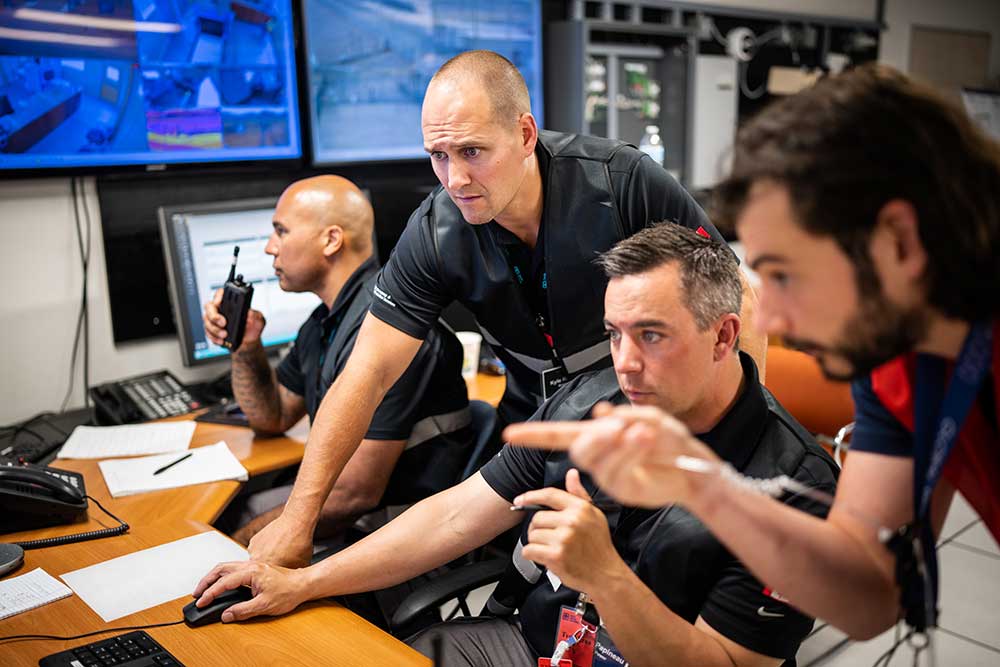

Technology addresses cyberattacks on nuclear power plants
With Idaho National Laboratory and alongside 45 security professionals from the Canadian Nuclear Laboratories, Sandia conducted an exercise at the Labs’ Nuclear Security Technology Complex to explore cyber and physical security gaps. The exercise successfully demonstrated a new Sandia-developed technology that emulates a cyberattack without compromising operation of a site’s critical systems, enabling more efficient and effective security analyses for civilian nuclear power plants. • 6000, INL, CNL





