
Solar Glare and Flux Analysis Tools
Measurement of reflected solar irradiance is receiving significant attention by industry, military, and government agencies to assess potential impacts of glint and glare from growing numbers of solar power installations around the world. This website describes tools to evaluate solar glare and receiver irradiance.
The Principal Investigator of this work is Dr. Clifford K. Ho (ckho@sandia.gov).
AVAILABILITY: Due to new cybersecurity restrictions at Sandia, SGHAT is now available for internal Sandia use only. All external use of SGHAT is restricted, even by other government or military users. The glare tool source code and algorithms are available for licensing from Sandia Laboratories. Interested parties can contact the licensing department. The following licensed SGHAT applications are available for public use: ForgeSolar glare analysis tools at www.forgesolar.com. If you have licensed SGHAT and would like to be listed, please contact us.
Solar Glare Hazard Analysis Tool
This tool determines when and where solar glare can occur throughout the year from a user-specified PV array as viewed from user-prescribed observation points. The potential ocular impact from the observed glare is also determined, along with a prediction of the annual energy production. Configurations can be quickly modified (e.g., tilt, orientation, shape, location) to identify a design that mitigates glare while maximizing energy production.
Meets FAA glare analysis requirements (78 FR 63276).
SGHAT requires a modern web browser
Tower Illuminance Model
The Tower Illuminance Model (“TIM”) is a real-time interactive concentrating solar field simulation. TIM models a concentrating tower (receiver), heliostat field, and potential reflected glare based on user-specified parameters such as field capacity, tower height and location. TIM provides a navigable 3D interface, allowing the user to “fly” around the field to determine the potential glare hazard from off-target heliostats. Various heliostat aiming strategies are available for specifying how heliostats behave when in standby mode. Strategies include annulus, point-per-group, up-aiming and single-point-focus. Additionally, TIM includes an avian path feature for approximating the irradiance and feather temperature of a bird flying through the field airspace.

Empirical Glare Analysis Tool
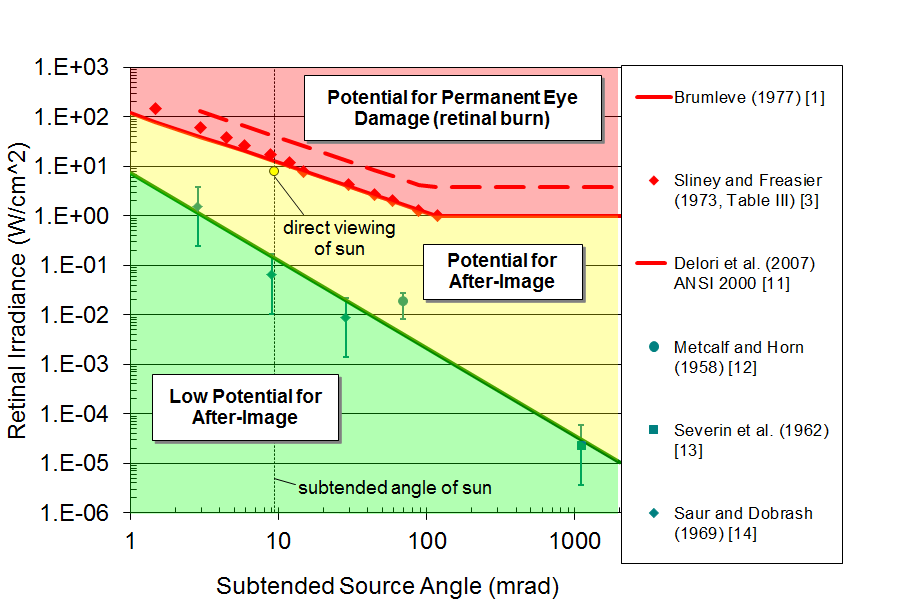
Empirically quantify glint and glare from reflected light and assess the potential impact (e.g. temporary after-image, retinal burn). No expensive equipment required – just upload photos of the glare and the sun.

Analytical Glare Estimation Tool
Analytically predict the potential impact (e.g. temporary after-image, retinal burn) of observed glare.
PHLUX Mapping Analysis Tool
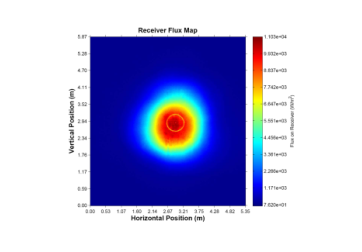
Empirically determine the irradiance distribution on a central receiver. No flux gauge needed – simply upload photos and fill in the details, and the tool does the rest.
Reflectivity Calculator Tool
Calculate the reflectivity of a receiver using only raw photos and details like location and heliostat characteristics.

