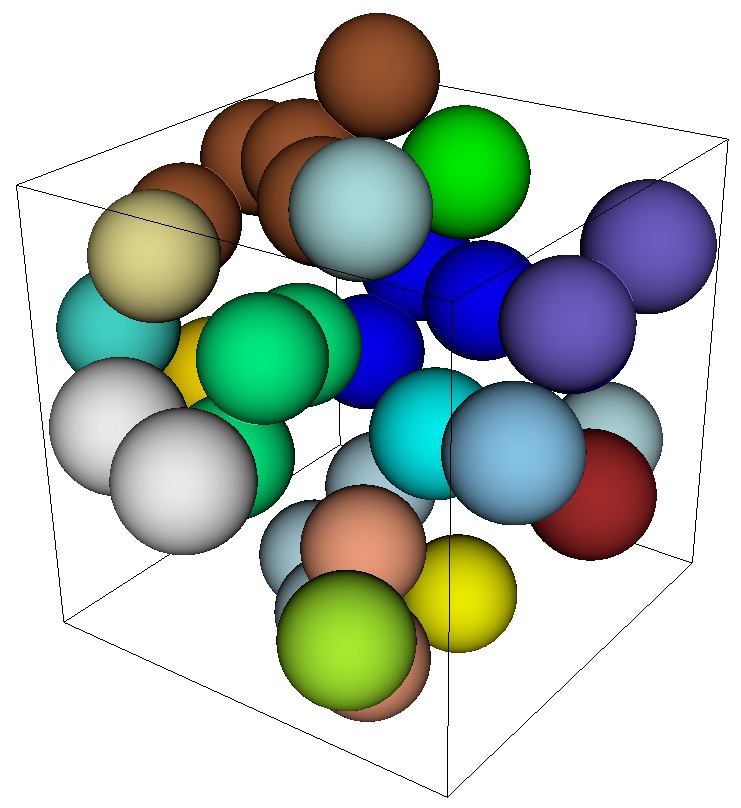
Periodic geometry used for example described in diatom file. RVE boundary shown with respect to the geometry.
Cubit 15.4 User Documentation
Options for controlling the execution of Sculpt. Sculpt is a parallel application that uses MPI to distribute and build the hex mesh on multiple processors. The -j or num_procs option is normally used to specify the number of processors to use. Sculpt will write a separate exodus file for each processor, which can be joined into a single file using the epu utility. While any number of processors may be used, you would normally use a -j value less than or equal to the number of cores available on your hardware.
Sculpt options can be specified directly from the command line using the "short" commands, or from an input file where the longer forms of the commands are used. Since an input file can be commented and modified, it is generally the recomended method for running Sculpt.
Process Control --process -pc --num_procs -j <arg> Number of processors requested --input_file -i <arg> File containing user input data --debug_processor -D <arg> Sleep to attach to processor for debug --debug_flag -dbf <arg> Dump debug info based on flag --quiet -qt Supress output --print_input -pi Print input values and defaults then stop --version -vs Print version number and exit --threads_process -tpp <arg> Number of threads per process --iproc -ip <arg> Number of processors in I direction --jproc -jp <arg> Number of processors in J direction --kproc -kp <arg> Number of processors in K direction --periodic -per Generate periodic mesh --check_periodic -cp <arg> CHeck for periodic geometry --periodic_axis -pax <arg> Axis periodicity is about --periodic_nodesets -pns <arg> Nodesets ids of master/slave nodesets --build_ghosts -bg Write ghost layers to exodus files for debug --vfrac_method -vm <arg> Set method for computing volume fractions Sculpt Command Summary
Command: num_procs Number of processors requested Input file command: num_procs <arg> Command line options: -j <arg> Argument Type: integer > 0Command Description:
The number of processors that Sculpt will use to generate the mesh. The Cartesian domain will be divided into roughly equal sizes based on this value and the mesh for each portion of the domain generated independently. Continuity across processor boundaries is maintained with MPI (Message Passing Interface). Each processor will write a separate Exodus II file to disk containing its portion of the domain. The Sandia SEACAS tool, "EPU" can be used to join parallel files into a single file.
If not specified on the command line, the number of processors used will be 1.
For additional control on the arrangement of processor domains see arguments iproc, jproc, kproc.
Command: input_file File containing user input data Input file command: input_file <arg> Command line options: -i <arg> Argument Type: file name with pathCommand Description:
Rather than specifying a complicated series of arguments on the command line, an input file may also be used. An input file is a simple text file containing all arguments and parameters to be used in the current sculpt run. Input files are normally expected to have a ".i" extension. Arguments used in the input file are limited to the Long Names indicated for each command.
User comments can also be made anywhere in the file but must follow a "$" sign. The argument assignments that are intended to be read must be contained within a "begin sculpt" and "end sculpt" block. All arguments may use upper or lower case and can optionally use "=" between the command and its parameter. The following is an example input file:
BEGIN SCULPT stl_file = "mygeom.stl" cell_size = 0.5 exodus_file = "mymesh" mesh_void = true END SCULPT
The following is an example of using an input file with sculpt:
sculpt -j 4 -i myinput.i
Note that the number of processors (-j) should always be used on the command line and cannot be included in the input file. Relative or absolute paths for files may also be used.
Command: debug_processor Sleep to attach to processor for debug Input file command: debug_processor <arg> Command line options: -D <arg> Argument Type: integer >= 0Command Description:
Used for debugging. All processes will sleep until the designated process is attached to a debugger. Note: value of 0 corresponds to first processor, 1 to second, etc.
Command: debug_flag Dump debug info based on flag Input file command: debug_flag <arg> Command line options: -dbf <arg> Argument Type: integer >= 0Command Description:
Used for debugging. Set flag to dump specific info based on the following:
0 Default, No debug output
1 Dump processor lost node info
2 Export Non-manifold resolution state as exodus file after each inner and outer iteration.
3 Export Defeature state as exodus file after each inner and outer iteration.
4 Export the Thickened state as exodus file after each material has been thickened.
Guaranteed Quality:
5 Turn off initial minimizer projection.
6 Use Non-manifold reversal case
7 Combine debug_flag 5 and 6
8 Use guaranteed quality laplacian color smoothing
9 Combine debug_flags 5,6 and 8
Command: quiet Supress output Input file command: quiet Command line options: -qtCommand Description:
Suppress any output to the command line from Sculpt as it is running.
Command: print_input Print input values and defaults then stop Input file command: print_input Command line options: -piCommand Description:
Display all input parameters and defaults used in the current Sculpt run to the output window and then stop. No mesh (or volume fractions) will be generated.
Command: version Print version number and exit Input file command: version Command line options: -vsCommand Description:
Prints Sculpt version information and exits.
Command: threads_process Number of threads per process Input file command: threads_process <arg> Command line options: -tpp <arg> Argument Type: integer > 0Command Description:
This option is currently experimental and under development. Sculpt may use shared memory parallelism to improve performance. When built with the Kokkos library, some algorithms in sculpt will use shared memory parallel threads in addition to MPI distributed memory parallelism (MPI+X). Currently this option is implemented only for surface and volume Laplacian smoothing algorithms. This option may not be available requiring a custom build of sculpt to be used. Check with developers if you would like to use this option.
Command: iproc Number of processors in I direction Input file command: iproc <arg> Command line options: -ip <arg> Argument Type: integer > 0Command Description:
Arguments iproc, jproc and kproc provide user control over the processor decomposition in I, J, and K directions respectively. iproc * jproc * kproc must equal the number of processors specified on the command line using the -j option.
Command: jproc Number of processors in J direction Input file command: jproc <arg> Command line options: -jp <arg> Argument Type: integer > 0Command Description:
Arguments iproc, jproc and kproc provide user control over the processor decomposition in I, J, and K directions respectively. iproc * jproc * kproc must equal the number of processors specified on the command line using the -j option.
Command: kproc Number of processors in K direction Input file command: kproc <arg> Command line options: -kp <arg> Argument Type: integer > 0Command Description:
Arguments iproc, jproc and kproc provide user control over the processor decomposition in I, J, and K directions respectively. iproc * jproc * kproc must equal the number of processors specified on the command line using the -j option.
Command: periodic Generate periodic mesh Input file command: periodic Command line options: -perCommand Description:
Generates a periodic mesh for either Cartesian or unstructured mesh input. Ensures that resulting mesh nodes and faces are precisely matching on opposite sides of the mesh.
Unstructured mesh input: When used with the --input_mesh option opposite sides of the mesh must be identified using pairs of leading and trailing nodesets using the --periodic_nodesets (-pns) option. Nodes in the nodeset pairs must be separated by a constant translation or rotation. If a rotation is used between leading and trailing nodesets, the --periodic_axis (-pax) option must be used. If not used, then the transformation is assumed to be pure translation. Input geometry is assumed to be periodic with a period equal to that of the input mesh. Results from non-periodic geometry used with the periodic option may be unpredictable. The following is an example of an input file that uses the periodic option on an unstructured input mesh:
BEGIN SCULPT diatom_file = geometry_file.diatom input_mesh = input_exodus_file.g exodus_file = output_exodus_file smooth = to_geometry capture = 5 capture_angle = 10 free_surface_sideset = 1000 gen_sidesets = input_mesh_and_free_surfaces periodic = true periodic_nodesets = 3224 3225 periodic_axis = 0 0 0 0 1 0 END SCULPT
Cartesian grid input: This option is often used for computational materials modeling. Sculpt can generate a true periodic mesh in a representative volume element (RVE) where meshes on all opposite faces of the RVE will precisely match. When used with a Cartesian grid, the --periodic_nodesets and --periodic_axis options are ignored. The following is an example sculpt input file that utilizes the --periodic option on a Cartesian grid with geometry defined in a diatom file. It also utilizes the --adapt_type option to automatically refine and the gen_sidesets = RVE option to generate sidesets at the six RVE faces.
BEGIN SCULPT diatom_file = spheres_periodic.diatom xmin = -18.705510 ymin = -18.705510 zmin = -18.705510 xmax = 18.705510 ymax = 18.705510 zmax = 18.705510 nelx = 38 nely = 38 nelz = 38 periodic = true defeature = 1 min_vol_cells = 10 adapt_type = vfrac_average adapt_levels = 2 adapt_threshold = 0.00001 gen_sidesets = RVE exodus_file = spheres_periodic mesh_void = true END SCULPTGeometry Requirements: In order to generate a valid periodic mesh, the input geometry must also be periodic and the bounding box parameters should span exactly one period of the geometry. To check the periodicity of the geometry and prescribed bounding box, see the check_periodic option. Note: The resulting mesh at the boundaries of the Cartesian grid (RVE) will not be projected to the planes of the bounding box. The result will be a "ragged" boundary in order to maintain periodicity between nodes on opposite sides of the mesh. Also note that results from the use of the periodic option may be undefined or unstable when used with non-periodic input geometry.

Periodic geometry used for example described in diatom file. RVE boundary shown with respect to the geometry.
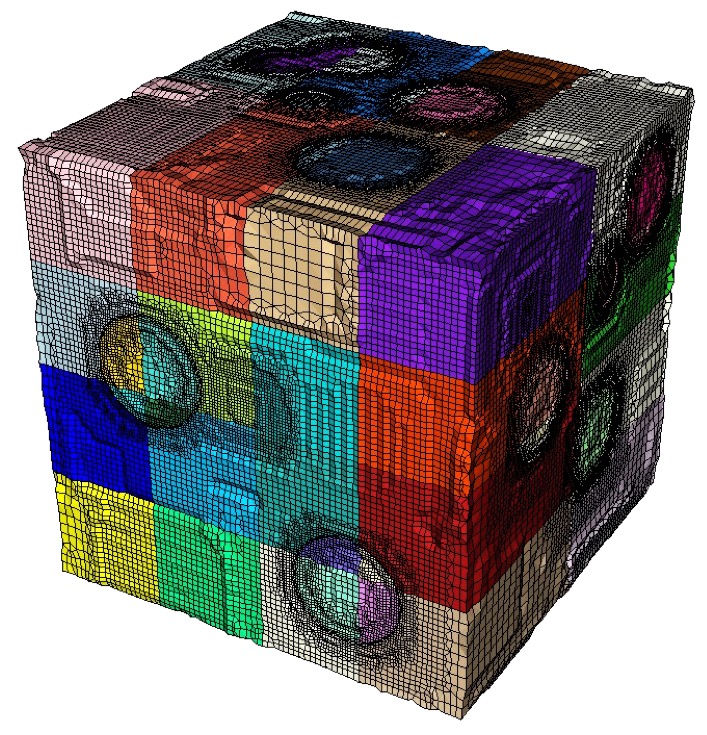

Resulting periodic mesh generated from example input.
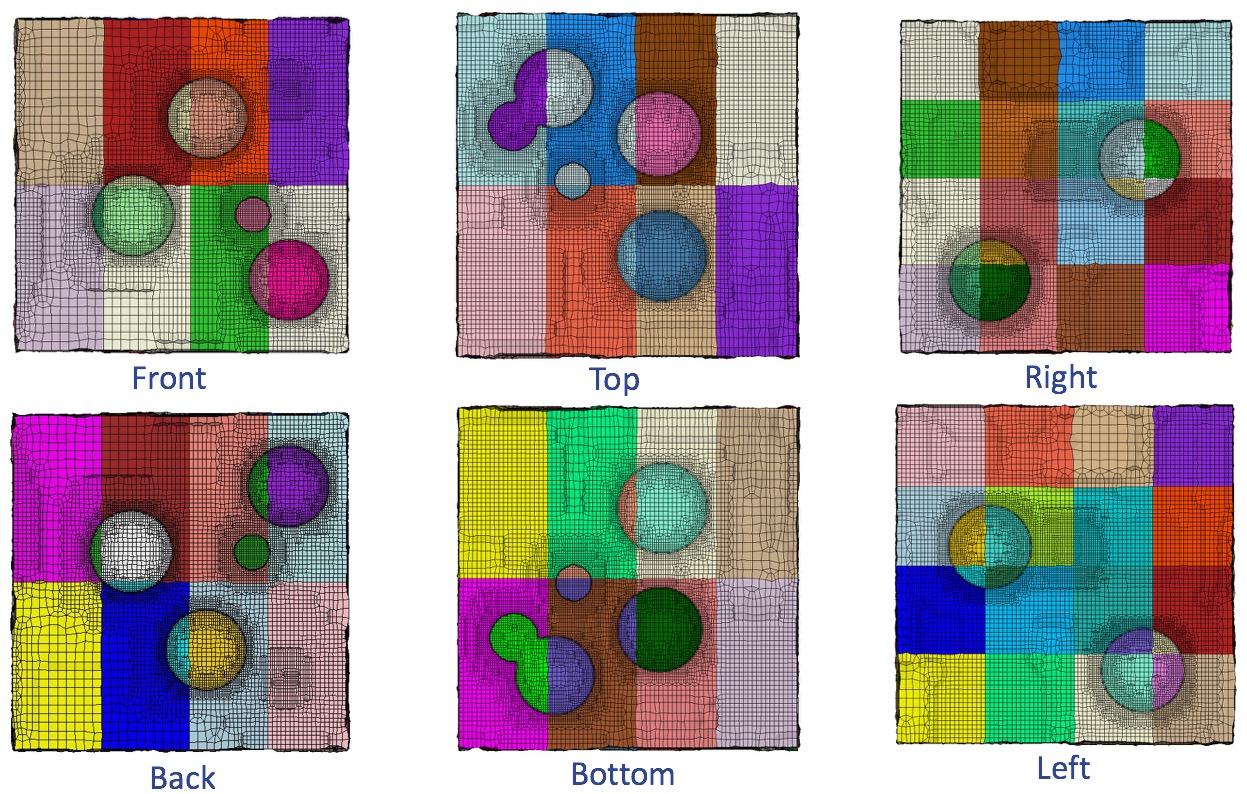
Six faces of the RVE from above example illustrating periodicity on a 32 processor decomposition. Note that top three images are a mirror image of the bottom three images.
Command: check_periodic CHeck for periodic geometry Input file command: check_periodic <arg> Command line options: -cp <arg> Argument Type: on, off, only Input arguments: off (0) on (1) only (2)Command Description:
When using the periodic option with a Cartesian base grid, the input geometry must be periodic with respect to the grid bounding box in order to meet the minimum requirements of a valid periodic mesh. The bounding box must span exactly one period in each dimension. If this requirement is not met, a valid mesh may still be generated, however, periodicity will not be guaranteed. The check_periodic option is used to check this requirement. Options:
Command: periodic_axis Axis periodicity is about Input file command: periodic_axis <arg> Command line options: -pax <arg> Argument Type: six floating point valuesCommand Description:
For an unstructured base grid, specifies an axis about which the nodes in the master (leading) nodesets will be rotated about to produce the slave (trailing) nodesets. Six floating point numbers are specified, the first three define the origin of the axis and the last three define the axis direction. This option must be used with --periodic (-per), --periodic_nodesets (-pns), and --input_mesh (-im) options. If the --periodic (-per) option is used without the --periodic_axis option, the transformation between leading and trailing nodesets is assumed to be pure translation.
Command: periodic_nodesets Nodesets ids of master/slave nodesets Input file command: periodic_nodesets <arg> Command line options: -pns <arg> Argument Type: integer(s) >= 0Command Description:
For an unstructured base grid, specifies the master-slave (leading-trailing) nodeset pairs. Master nodesets should be able to be translated or rotated about a specified axis to produce the nodes in the slave nodesets. Nodesets must be specified in pairs, where each master (leading) nodeset corresponds to a single slave (trailing) nodeset. Each nodeset pair must maintain an identical translation or rotation. If a rotation is used, the axis and origin of rotation must be specified with the --periodic_axis (-pax) option. This option should be used with --periodic (-per), --periodic_nodesets (-pns), and --input_mesh (-im) options.)

Unstructured input mesh used to generate periodic mesh. Matching leading and trailing nodesets are defined in the exodus file.
Command: build_ghosts Write ghost layers to exodus files for debug Input file command: build_ghosts Command line options: -bgCommand Description:
If set, this option will dump the ghost hexes at the boundaries of processor domains to the exodus files. This is used only for debugging.
Command: vfrac_method Set method for computing volume fractions Input file command: vfrac_method <arg> Command line options: -vm <arg> Argument Type: integer (1, 2) Input arguments: cth (0) cth (1) r3d (2)Command Description:
Sets the method used for computing volume fractions from geometry input. Two options are currently available:
CTH (1): The default method. It uses the CTH third party library from Sandia Laboratories for approximating intersections using an adaptive ray firing method to determine inside-outside status of multiple locations within a grid cell. This methid can be used with STL and all valid primitive types defined by the diatom format.
R3D (2): Uses the R3D third party library developed by Los Alamos Laboratories. Machine precision intersection calculations are performed to generate acurate volume fractions from the STL description. This method is valid for STL and diatom input packages specifying STL input files. Non STL format geometry defined in the diatom file will be ignored for this format.