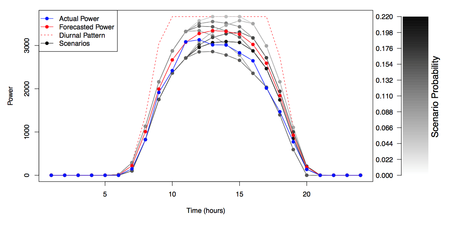
As part of DOE/ARPA-e’s NODES (Network Optimized Distributed Energy Systems) program, researchers at Sandia National Laboratories – with partners at Arizona State University and Nexant, Inc. – are working to develop advanced optimization algorithms for power grid operations, which directly account for uncertainty associated with forecasts of renewables (e.g., wind and solar) power production. By modeling and addressing such uncertainty directly, power systems operations will be able to integrate very large (>50% penetration levels) quantities of renewable energy, in a reliable and cost-effective manner. Feasibility studies are being conducted on real models of large-scale power system operators, including the Midwest Independent System Operator (MISO) and the Pennsylvania-Jersey-Maryland (PJM) system operator. (Summary: Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories, with partners at Arizona State University and Nexant Inc., are developing advanced strategies for enabling cost-effective and reliable integration of very large quantities of renewables power on the electric power grid.)