Award, April 3, 2014 • Invited Talk, Workshop on New Challenges in Scheduling Theory.
Search
“Optimization-based modeling – a new strategy for predictive simulations. Part 1”
Award, May 7, 2011 • Invited Talk, 8th Int. Conf. Large Scale Sci. Comp., June 2011, Sozopol.
1460 researchers awarded contract to provide test and evaluation for IARPA MICrONS Program
News Article, September 1, 2016 • 1460 researchers recently won a contract to provide test and evaluation support for a new IARPA program: Machine Intelligence from Cortical Networks (MICrONS). The MICrONS program aims to advance a new generation of neural-inspired machine learning algorithms by reverse engineering the algorithms and computations of the brain. The Sandia team’s...
2011 National Nuclear Security Administration Defense Programs Award of Excellence
Award, September 1, 2011 • Other external recognition, National Nuclear Security Administration.
2013 Dakota releases provide users an array of new features
News Article, May 1, 2013 • Dakota version 5.3, released 1/31/2013, and its partner version 5.3.1, released 5/15/2013, feature new adaptive, sparse, and surrogate-based UQ methods, new Bayesian calibration methods, and improvements to discrete optimization. The new versions also include enhancements to the testing infrastructure, core framework, and portability (including to native Windows). The Dakota user...
2017 Defense Programs Award of Excellence
Award, October 1, 2017 • Other external recognition, National Nuclear Security Administration. Trinity High Performance Computing Team for significant contributions to the Stockpile Stewardship Program
2020 Rising Stars Workshop Supports Women in Computational & Data Sciences
News Article, January 1, 2021 • Rising Stars in Computational & Data Sciences is an intensive academic and research career workshop series for women graduate students and postdocs. Co-organized by Sandia and UT-Austin’s Oden Institute for Computational Engineering & Sciences, Rising Stars brings together top women PhD students and postdocs for technical talks, panels, and networking...

5th Annual NICE Workshop
News Article, June 1, 2017 • Neural computing researchers at Sandia National Laboratories helped organize and facilitate the 5th Neuro-Inspired Computational Elements (NICE) Workshop at IBM Almaden in San Jose, CA. The meeting was attended by neural computing researchers from numerous universities, computing software and hardware companies, and national laboratories (including LLNL, LANL, and Oak Ridge)....
A Lightweight Trilinos Solver Interface for Fortran-Based Multiphysics Applications
News Article, April 1, 2016 • Sandia researchers have previously developed a lightweight interface software layer that makes linear solvers from the Sandia Trilinos project accessible to the Fortran-based multiphase flow solver suite named MFIX (https://mfix.netl.doe.gov), originally developed by the National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL). Under a current Office of Fossil Energy project named "MFIX-DEM Phi",...
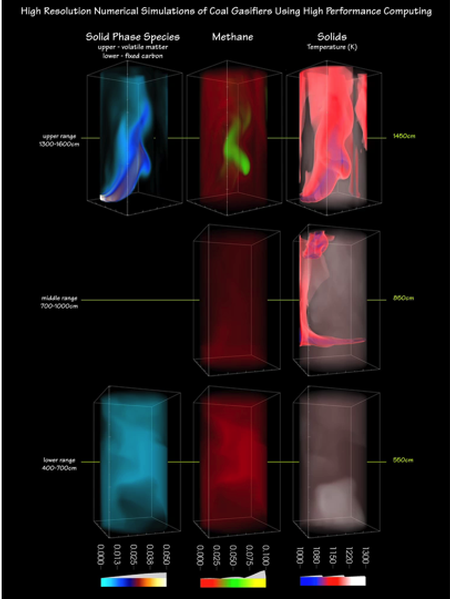
A Locally Conservative, Discontinuous Least-squares Finite Element for the Stokes Equations
Award, July 19, 2011 • Invited Talk, ICIAM 11, Vancouver. Presented at special session on "Advances in locally mass conservative discretizations for fluid flows"
A new optimization-based mesh correction method with volume and convexity constraints.
News Article, April 1, 2016 • Mesh motion is at the core of many numerical methods for time dependent flow and structure problems. Examples include Lagrangian hydrodynamics methods, in which the mesh evolves with time in order to track deformations of the problem domain, and the related Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian methods, which incorporate a mesh rezoning step...
A new, optimization-based coupling strategy for nonlocal and local diffusion models
News Article, April 1, 2016 • The use of nonlocal models in science and engineering applications has been steadily increasing over the past decade. The ability of nonlocal theories to accurately capture effects that are difficult or impossible to represent by local partial differential equation (PDE) models motivates and drives the interest in a wide range...
A new, optimization-based coupling strategy for nonlocal and local diffusion models
News Article, December 1, 2015 • The use of nonlocal models in science and engineering applications has been steadily increasing over the past decade. The ability of nonlocal theories to accurately capture effects that are difficult or impossible to represent by local partial differential equation (PDE) models motivates and drives the interest in a wide range...
Accelerating development of semiconductor qubits through better computational modeling
News Article, May 1, 2016 • John King Gamble and N. Tobias Jacobson Non-Conventional Computing Technologies Center for Computational Research

ACES and NERSC form partnership for next-generation supercomputers, an unprecedented collaboration between NNSA and the Office of Science
News Article, March 1, 2013 • The Alliance for Computing at Extreme Scale (ACES, a collaboration of the NNSA’s Los Alamos National Laboratory and Sandia National Laboratories) and the Office of Science’s National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) have fully integrated as a team as they work towards their respective next-generation supercomputer deployments. The goal...
Additive Decomposition of Multiphysics Problems
Award, February 27, 2011 • Invited Talk, 2011 SIAM CS/E Conference.
Addressing Challenges in Reduced-Order Modeling
News Article, March 1, 2016 • https://sinews.siam.org/DetailsPage/tabid/607/ArticleID/745/Addressing-Challenges-in-Reduced-Order-Modeling.aspx
Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Memory Resolution, Pattern Separation, or Both?
Award, March 12, 2013 • Invited Talk, University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Neuroscience Program.
Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Memory Resolution, Pattern Separation, or Both?
Award, April 10, 2013 • Invited Talk, Boston University Biomedical Engineering.
Advanced Device Technologies
Focus Area • Despite the vast computational power available in today's extreme-scale computing systems, there are still certain types of problems for which that power is inadequate and silicon-based computing devices will likely never be able to solve. Sandia is exploring technologies necessary to enable a new paradigm of computing that goes beyond...
Advanced Memory Technology (AMT)
Project • Under the Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) program, computer simulation capabilities are developed to analyze and predict the performance, safety, and reliability of nuclear weapons and to certify their functionality. Historically, the performance of many critical NNSA mission applications have been limited by memory bandwidth and latency. Memory bandwidth has...

Advanced Release of Draft Technical Specifications for Crossroads
News Article, February 1, 2016 • The first version of the draft technical specifications for Crossroads were released on November 1st 2015 to the vendor community for comment. Crossroads, one of two platforms targeted for delivery in 2020, will be the NNSA’s third Advanced Technology System. Crossroads will be the second platform procured as part of...

Advanced Tri-lab Software Environment (ATSE)
Project • The Advanced Tri-lab Software Environment (ATSE) is an integrated software environment that provides a software ecosystem for leading-edge prototype high-performance computing (HPC) systems. By leveraging vendor software alongside open-source software throughout the stack, ATSE continually pushes forward the computing environment experience for the Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) program on...

Advisory Board Membership: National Research Council of the National Academies Standing Committee on Operational Science & Technology Option for Defeating IEDs
Award, January 1, 2011 • Society/professional leadership, Professional Society.
Aeras Project Develops Next-Generation Atmosphere Model
News Article, April 1, 2016 • The goal of the Aeras LDRD project is to develop a next-generation atmosphere model suitable for a global climate model, with advanced capabilities such as performance portability and embedded uncertainty quantification (UQ). Performance portability will allow us to run our code very efficiently on a diverse set of current and...
Results 1–25 of 480